The prevalence of manipulative dark patterns in eCommerce platforms has grown dramatically in the past decade. A 2022 report from the European Commission found that 97% of popular mobile apps incorporate at least one deceptive design element intended to sway consumer decisions.
As identified by Harry Brignull in 2010, these techniques exploit psychological vulnerabilities to nudge people toward purchases or subscriptions they may not truly want. Research from UChicago/Princeton revealed that 10% of major online retailers implement dark patterns on their sites.
Such covert tactics can effectively alter shopping behavior without consumers realizing it, as a Spotify study showed 47% of people abandoned items in their carts due to unexpected fees unveiled at checkout.
This comprehensive guide aims to increase awareness of how some brands manipulate shoppers through design and highlights what to avoid when shopping online. It also identifies common misleading practices and provides strategies for navigating online shopping while avoiding manipulation.
What Are Dark Patterns in eCommerce?
Dark patterns in eCommerce refer to sneaky or underhanded user interface techniques employed by some sites to subtly steer visitors’ choices in a direction that prioritizes commercial goals over consumer autonomy.
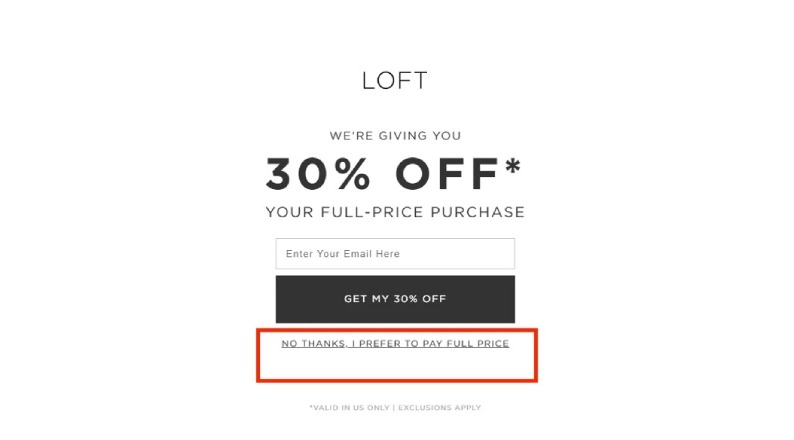
Whether through strategic placement of options, framing effects, or obscured information, these designs leverage principles of influence to potentially guide online shopping behavior via insidious means rather than informed consent.
Origin and Definition
The idea of “dark patterns” comes from Harry Brignull, a British designer who first noticed misleading website designs in 2010. Dark patterns are interfaces created to sneakily influence the choices people make.
They trick users into decisions they may not have otherwise. These techniques especially target people who don’t have much time or tech experience to realize they are being secretly swayed into clicking on something.
Why Businesses Use Them
Companies employ dark patterns primarily to extract three key resources from users: money, data, and attention. Additionally, the rise of A/B testing has enabled businesses to perfect these manipulative techniques through extensive experimentation.
Research from the University of Zurich revealed that dark patterns appeared in 95% of 240 free, trending apps sampled from the Google Play store.
Common Examples of How Some Brands Manipulate Shoppers
Several prevalent dark patterns plague the eCommerce landscape:
- Hidden Costs and Fees: Retailers often conceal mandatory charges until the final stages of checkout. A notable example includes GrubHub, which agreed to pay $3.50 million to settle a lawsuit regarding hidden fees.
- Forced Continuity: This pattern involves automatically enrolling users into subscription services after free trials without clear notification. Many companies deliberately make the cancelation process complex, requiring customers to navigate through multiple steps or make phone calls to customer service.
- Misleading Product Information: Some retailers employ bait-and-switch or drip pricing techniques. Bait-and-switch refers to advertising items at low costs before mandating more expensive substitutes at checkout. Drip pricing slowly reveals extra mandatory fees throughout the purchase process, increasing the final amount spent by consumers by around 20% compared to the original displayed total.
- Privacy Manipulation: Websites design cookie consent dialogs in ways that manipulate users into agreeing to data tracking more often than if presented simply. While informed consent is best, techniques are employed to shift more users towards approval when asked to consent to tracking.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has noted a marked increase in sophisticated dark patterns across digital platforms. These deceptive practices have evolved from simple pre-checked boxes to complex analytical techniques that exploit consumer behavior patterns.
Through strategic design choices, retailers create interfaces that obstruct users from making choices that don’t benefit the company. For instance, the FTC recently filed a lawsuit against Amazon regarding its use of obstruction tactics when customers attempted to unsubscribe from Prime online.
Similarly, many businesses implement “roach motel” designs, making account creation straightforward but deliberately complicating the cancelation process. Recognizing these common examples can help you avoid falling victim to them.
Most Common Dark Pattern Types in Online Shopping
Online retailers employ an array of deceptive practices that exploit consumer psychology and shopping behaviors. These tactics are designed to influence purchasing decisions in subtle yet impactful ways.
Hidden Costs and Fees
Consumer Reports estimates that hidden fees, a common dark pattern in eCommerce, cost the average family of four over $3,200 annually. These unexpected charges often surface at the final stages of checkout, after shoppers have invested time selecting products.
Notably, food delivery apps charge restaurants commissions between 15% to 30% on orders, costs that ultimately get passed to consumers through inflated menu prices.
A prime example involves the fashion retailer Shein, which adds undisclosed “handling” fees during checkout that vary based on order size and item quantity.
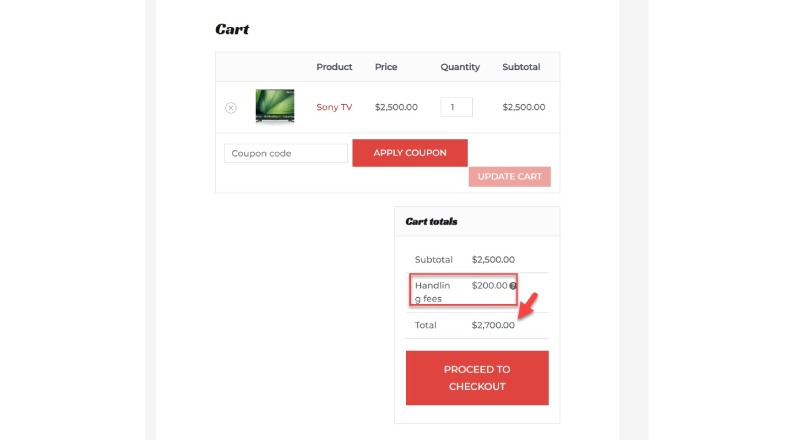
Consequently, GrubHub agreed to pay $3.5 million to settle a lawsuit regarding such concealed charges.
Forced Account Creation
Research reveals that forced registration represents a significant dark pattern across eCommerce platforms. The RealReal and JustFab exemplify this practice – while allowing browsing, they mandate account creation before adding items to a cart.
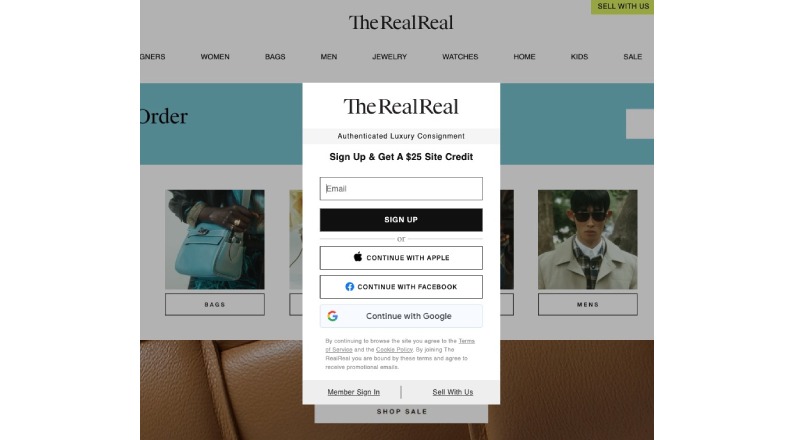
This tactic enables companies to harvest valuable user data for marketing purpose s or sell to third parties.
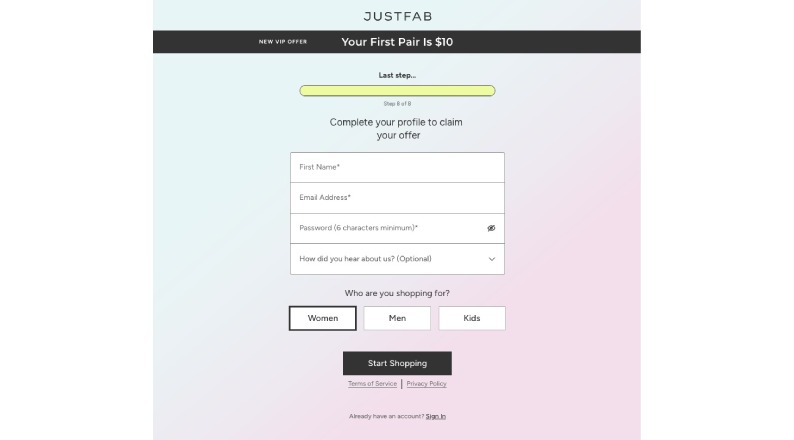
Although businesses sometimes need basic information to provide services, forced registration becomes problematic when companies demand unnecessary personal details.
This practice often results in adverse outcomes, driving potential customers to competitors who don’t employ such aggressive data collection methods.
Misleading Product Information
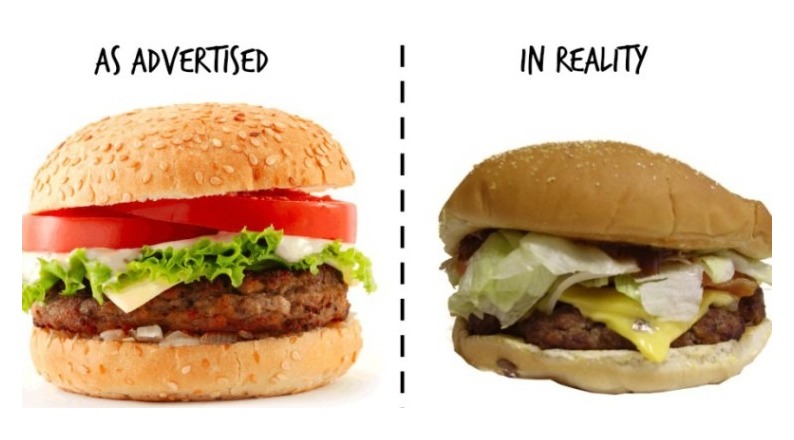
Product Information Failures (PIFs) significantly impact shopper behavior and retailer reputation.
Research indicates that 40% of websites mislead shoppers with inaccurate content. The most severe issues involve:
- Missing product images and incorrect pricing on multi-buy deals
- Altered or fake product photos that don’t accurately represent items
- Incomplete or erroneous product descriptions affecting 10% of eCommerce websites
These deceptive practices lead to increased return rates – two to three times higher than in-store purchases.
Subscription Tricks
Subscription-based dark patterns, a common tactic in eCommerce, often manifest through forced continuity and complex cancelation processes.

Companies frequently enroll users in premium subscriptions after free trials without clear notification. Research shows this practice impacts customer retention – the primary reason for unsubscribing stems from a perceived lack of value and complicated pricing structures.
StubHub’s pricing experiments revealed that concealing fees through drip pricing increased revenue by 20%, even among experienced users. However, this short-term gain comes at a cost – businesses face increasing regulatory scrutiny.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has proposed a “click to cancel” provision requiring companies to make subscription cancelation as straightforward as sign-up.
The subscription model demands continuous value delivery to justify recurring payments. Yet, many businesses overlook critical aspects like:
- Transparent pricing communication
- Flexible subscription management options
- Clear cancelation procedures
- Regular rotation of inventory and personalization
Undoubtedly, these manipulative practices affect consumer trust and brand reputation. The European Union has already implemented regulations requiring all-in pricing, where final costs, including fees and taxes, must be displayed upfront.
This approach enables consumers to make informed comparisons and purchasing decisions without falling prey to hidden charges or deceptive subscription tactics.
How Dark Patterns in eCommerce Trick Online Shoppers
Behind every deceptive design choice lies a calculated strategy to influence consumer behavior. A Princeton University study revealed that these manipulative interfaces appear on over 11% of nearly 11,000 shopping websites.
Psychological Manipulation Tactics
Online retailers strategically employ psychological triggers that bypass conscious decision-making processes. Research indicates that more than 40% of consumers have faced unexpected financial consequences due to these manipulative design elements.
The manipulation often begins with bait-and-switch tactics, where shoppers see attractive prices only to discover the advertised items are “sold out,” followed by suggestions for pricier alternatives.
Retailers also exploit the power of social validation – studies show the number of reviews can influence sales more strongly than the actual rating quality.
Another powerful tactic involves creating artificial scarcity. Princeton researchers uncovered hundreds of cases where websites displayed countdown timers suggesting deals would expire soon, even though the offers remained valid indefinitely.
These false urgency messages tap into the Fear of Missing Out (FOMO), compelling shoppers to make rushed decisions.
Exploiting Cognitive Biases
Dark patterns capitalize on several inherent human psychological tendencies:
- Anchoring Effect: Shoppers disproportionately rely on the first piece of information they encounter when making decisions. Retailers exploit this by prominently displaying higher-priced items first, making subsequent options seem more reasonable.
The manipulation extends through multiple cognitive shortcuts:
- Loss Aversion: Studies show people prioritize avoiding losses over acquiring equivalent gains. Retailers leverage this by framing opt-out choices as missed opportunities.
- Default Bias: Research demonstrates users tend to accept pre-selected options. This explains why major retailers employ pre-ticked boxes and highlighted default choices.
- Scarcity Bias: People assign higher value to items portrayed as limited. Online stores exploit this through “low stock” warnings and exclusive offers.
Princeton’s research found that users exposed to mild dark patterns were twice as likely to make unintended purchases, whereas aggressive patterns led to a nearly fourfold increase in unplanned buying.
Strikingly, the study also revealed that when dark patterns were employed, the actual cost of items became irrelevant – decision architecture, rather than price, drove purchasing choices.
These manipulative techniques prove especially effective because they target subconscious decision-making processes. Studies suggest up to 50% of grocery purchases stem from impulsiveness, with over 87% of shoppers making unplanned buys.
The psychological impact extends beyond the wallet – impulse purchases triggered by dark patterns often lead to feelings of shame, guilt, anxiety, and, in some cases, shopping addiction.
The effectiveness of these tactics varies based on education levels. Research indicates less educated consumers show significantly higher susceptibility to mild dark patterns compared to their well-educated counterparts. This disparity raises serious ethical concerns about the disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations.
Online shopping platforms have perfected these manipulation techniques through extensive A/B testing and behavioral analysis. The dopamine release associated with anticipated purchases creates a temporary pleasure boost, which retailers exploit through carefully crafted user interfaces.
This neurological response can lead some consumers into patterns of excessive buying as they chase the momentary high of making purchases.
Real Impact on Customer Trust
The growing sophistication of manipulative design practices across digital marketplaces raises serious concerns about their impact on consumer relationships.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Effects
While deceptive design patterns might boost immediate sales, their lasting consequences prove detrimental to business success. Research demonstrates that 56% of consumers reported losing trust in websites after encountering manipulative design practices.
The short-term gains often manifest through increased conversions and quick profits. Yet, these temporary advantages come at a steep price – the FTC reports that companies using dark patterns face mounting legal challenges, with settlements reaching tens of millions of dollars.
In the long run, businesses employing these tactics experience:
- Financial losses from customer churn
- Increased regulatory scrutiny
- Higher customer acquisition costs
- Reduced market competitiveness
Brand Reputation Damage
The widespread adoption of social media amplifies the negative impact of dark patterns on brand perception. Indeed, 43% of consumers completely stopped purchasing from retailers after experiencing manipulative design tactics.
Brand damage occurs through multiple channels:
- Social media backlash from frustrated customers
- Negative online reviews affecting purchase decisions
- Word-of-mouth warnings among consumer networks
- Public criticism from consumer advocacy groups
These consequences highlight the importance of transparency and ethical design practices in maintaining consumer trust and long-term brand loyalty.
Customer Loyalty Impact
The erosion of trust fundamentally undermines customer loyalty programs. As previously stated, over 40% of consumers reported financial harm from dark patterns, including being rushed through confusing purchase processes or misled into buying more expensive products.
The damage to customer relationships manifests in several ways:
- Decreased repeat purchase rates
- Reduced customer lifetime value
- Lower referral rates
- Heightened skepticism toward future promotions
Manipulative marketers often prioritize immediate gains over building lasting customer relationships. This short-sighted approach typically backfires as consumers eventually uncover deceptive practices and initiate public backlash.
Dark patterns undermine consumer autonomy and foster a digital environment where users feel unsafe and manipulated. This erosion of trust poses a significant threat to the efficient functioning of digital marketplaces.
The impact becomes particularly evident in customer retention metrics.
Clients who encounter dark patterns develop negative brand perceptions and are less likely to engage in repeat business. These customers often feel exploited rather than valued, leading them to share their unpleasant experiences with others.
Ultimately, while dark patterns might drive immediate profits, they create lasting damage to customer relationships, increase customer churn, and potentially trigger legal consequences.
As consumers become increasingly aware of these tactics and regulations, tighten, businesses relying on deceptive design practices risk trading short-term gains for permanent reputation damage.
Spotting Dark Patterns While Shopping: What to Avoid
Recognizing how some brands manipulate shoppers through design elements requires vigilance while shopping online. As we’ve seen, dark patterns are common on eCommerce websites, making it crucial for shoppers to stay alert.
Common Red Flags
Several warning signs indicate potential manipulation in online stores. Multiple orders from different credit cards shipping to the same address stand out as a primary concern. Likewise, data inconsistencies between billing and shipping information merit careful attention.
Shoppers should watch for:
- Sudden price changes during checkout
- Countdown timers that reset upon page refresh
- Pre-selected add-ons in shopping carts
- Multiple pop-ups requesting email signups or notifications
Where To Look Carefully
The checkout process demands heightened attention. Retailers often add “handling” fees at the final payment stage that remain invisible in the shopping cart. Therefore, examining every line item becomes essential.
Critical areas requiring scrutiny:
- Privacy settings and data collection options
- Subscription terms and cancelation policies
- Price breakdowns, including shipping costs
- Account creation requirements
Many websites use false hierarchy tactics, making certain options more visually prominent.
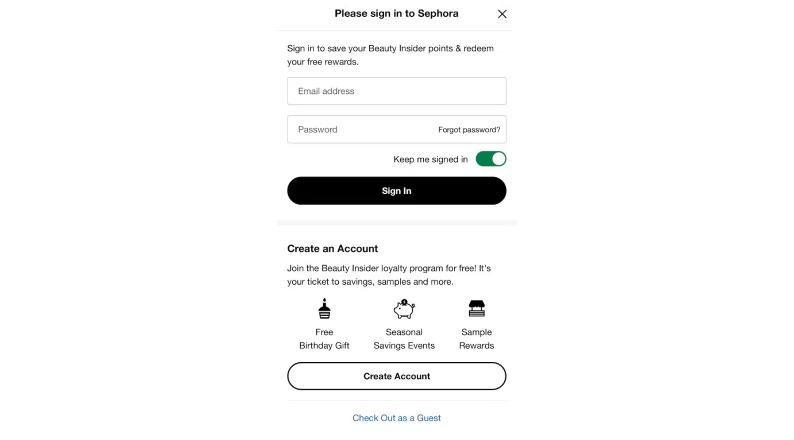
For example, the “create account” button might appear more noticeable than the “checkout as guest” option.
What Questions To Ask
Prior to completing purchases, shoppers should consider several key questions. First, does the final price match the advertised cost? Some companies employ hidden cost tactics, so it’s important to verify this.
Subsequently, examine whether shipping addresses align with billing information, as mismatches often signal deceptive practices.
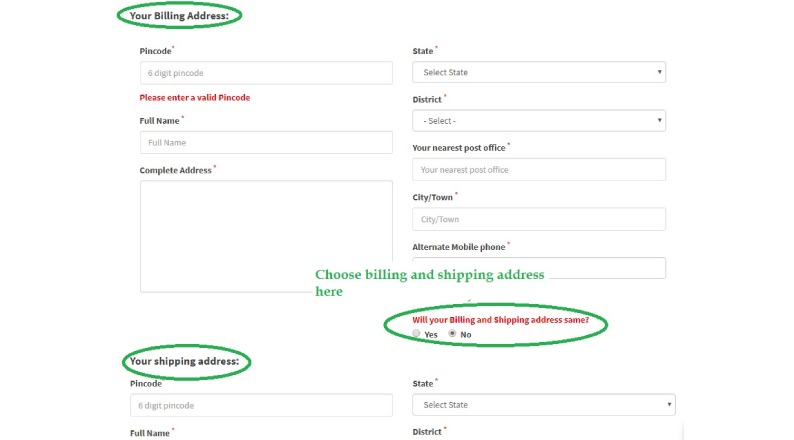
Additional questions worth considering:
- Are urgency claims genuine or artificial?
- Does the site require unnecessary personal information?
- Can subscriptions be canceled easily?
- Do privacy settings maximize data collection by default?
Understanding privacy implications becomes paramount before proceeding with purchases.
The Federal Trade Commission advises scrutinizing websites that display unusual purchasing patterns or inconsistent pricing. Straightforward language and clear pricing indicate trustworthy retailers, whereas confusing terms or double negatives often mask deceptive practices.
A 2023 survey revealed that over 40% of consumers experienced unplanned financial consequences from dark patterns.
Therefore, maintaining awareness of these tactics helps protect against manipulation. Shoppers should trust their instincts – if something feels questionable, it likely warrants further investigation.
Conclusion
Recognizing how some brands manipulate shoppers through dark patterns in eCommerce is vital for making informed decisions. Hidden fees, forced account creation, misleading information, and tricky subscription tactics are common pitfalls.
By staying vigilant and knowing what to avoid, consumers can protect themselves and maintain control over their purchases. Ethical design and transparency are crucial for businesses aiming to build long-term trust.
As online shopping continues to grow, awareness of these manipulative practices empowers consumers to demand and support fair and honest eCommerce experiences.
By being informed and cautious, shoppers can navigate the digital marketplace with confidence, ensuring their shopping experiences are both enjoyable and secure.
Acowebs are the developers of the WooCommerce Product Labels which let customers include custom product labels or product badges for the WooCommerce products. WooCommerce sales badges plugin provides you with different label styles and customizations for labels. It offers a easy-to-use UI to add labels to the selected products or categories and woocommerce email customizer using which you can easily build and customize WooCommerce emails with a drag-and-drop user interface.









 Login
Login
 Cart
Cart