Table of Contents
Product validation is a critical process in the journey from concept to market, ensuring that a product meets specific requirements and is fit for consumer use.
As the initial step in forging a new product or business it involves a meticulous evaluation of the product’s functionality, performance, and market suitability.
This process is not only foundational but also adopts a scientific approach, aiming to secure and uphold a product-market fit while facilitating research in a manner that is both rapid and efficient.
The essence of product validation lies in its dual role as both a preventive measure and a strategy for continuous improvement, spanning the entire lifecycle of a product. Through rigorous testing and feedback, it acts as an external verification of the product’s capability to solve customer problems effectively.
This article will discuss and navigate through the various stages of the product validation process and explore strategic approaches, including leveraging digital tools and learning from successful case studies, to enhance this crucial exercise.
Defining Product Validation
Product validation is a critical process that assesses whether a product’s features meet the needs and alleviate the pain points of both current and potential customers. This process is not merely a one-off event during the proof of concept, but a continuous cycle that persists throughout the entire lifecycle of the product.
Essential to bringing a product to market, product validation ensures that the product is prepared for consumer use, allowing for necessary adjustments before its launch which helps in avoiding expensive errors.
The scientific approach of product validation aims to achieve and maintain a product-market fit. This method provides a scalable way to conduct research swiftly and more effectively. By repeatedly testing and evaluating a product, this process verifies that the product will fulfill customer needs.
It also confirms market demand before substantial investments are made in manufacturing or development, significantly reducing business risks associated with producing something that might lack market demand.
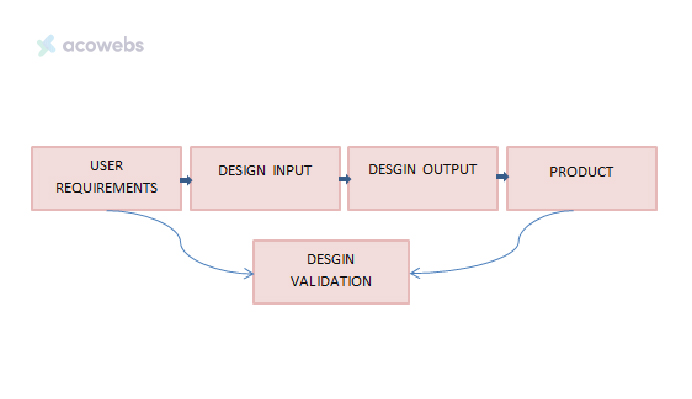
After a product passes through the verification phase, product validation is performed. This phase demonstrates that the final product satisfies its intended use when operated within its intended environment.
It ensures proper integration of human factors into the system and resolves any issues identified prior to delivery.
The product validation process encompasses several critical steps, including defining what people need, learning who the audience is, running a market analysis, and determining if there is a desire for the product.
These steps collectively ensure that the product not only meets technical specifications but also resonates well with its target market.
Why Product Validation Matters
Product validation is essential because it directly impacts a business’s ability to deliver solutions that meet market needs and consumer expectations.
By engaging in this process, companies can discover if potential customers genuinely desire the solution they are envisioning.
This step is crucial as it removes the guesswork by understanding customers’ behaviors, challenges, and current solutions, ensuring that the product developed is not just innovative but also desired.
1. Risk Reduction and Market Fit
Product validation is an important step that can significantly decrease the risk of business failure. Through validation, businesses gain useful insights to reasonably predict whether their product will be purchased, thus enhancing the chances of success.
By validating a product first, companies can avoid heavily investing in an idea that may not resonate with the market. This saves valuable time, effort, and capital that could otherwise be wasted.
Unfortunately, about 90% of startups fail, and lack of market need is often a key reason why. Ensuring a product-market fit through validation helps mitigate this substantial risk that many fledgling companies unfortunately face.
2. Customer-Centric Product Development
Product validation is an important part of developing solutions with customers in mind. By soliciting input from prospective users early in the process, businesses gain insights that help align their offerings with real needs and preferences.
Gathering feedback provides an opportunity to refine a product by addressing what customers say is most important. This customer-first approach builds confidence because it demonstrates the company’s commitment to satisfying users.
With validation, companies can optimize their solution to increase the chances it is well-suited for its target market and those it aims to serve.
3. Efficient Use of Resources
Product validation is an important step that helps ensure efficient use of business resources. By gaining customer input and feedback during validation, companies can make well-informed go/no-go decisions about advancing an idea into the development phase.
Proceeding only with product concepts that demonstrate real market potential helps prevent wasted expenditure on solutions unlikely to succeed. Regular validation also gives opportunities to continuously refine and strengthen a product’s fit based on insights from prospective users.
This increases the chances an offering will resonate and be adopted when introduced to the target market.
The Essential Steps in the Product Validation Process
Identify Customer Needs and Market Fit
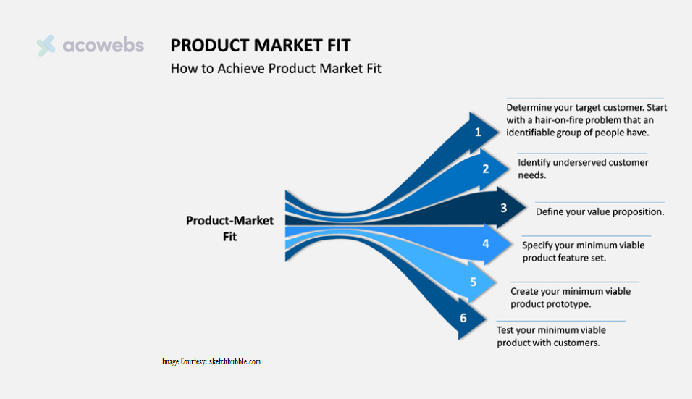
- Define What People Need: Start by identifying the core needs and problems of your target audience. Understand their current pain points and the solutions they are using. This foundational step ensures the product concept is relevant and necessary.
- Learn Who Your Audience Is: Gathering insights into the prospective customer base is crucial for validation. Conducting focus groups and surveys and analyzing similar offerings helps clearly define the target demographic for a product.
- Run a Market Analysis: Assess the market size, competition, and price points. This analysis helps confirm the existence of a viable market for your product.
- Figure Out If People Want the Product: Creating an initial prototype or Minimum Viable Product (MVP) allows testing directly with potential users. Their feedback provides an invaluable perspective on satisfying real needs and determining if the proposed product is a good solution for the intended market.
This step is pivotal to assessing whether a concept has legitimacy or requires adjustment based on consumer input.
Conduct Thorough Competitive and Demand Analysis
- Conduct Competitive Analysis: Investigate your competitors to understand their strengths and weaknesses. This information will help you position your product to capitalize on market gaps.
- Research Existing Demand: Utilize tools like Google Trends and Ahrefs to analyze search volumes and existing demand for your product. This data provides insights into market interest and potential sales volume.
Engage with Potential Customers

- Create a Feedback Survey: Design a survey to collect detailed feedback on your MVP from potential customers. This direct feedback is invaluable for iterative development.
- Start a Crowdfunding Campaign: Platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo can be used not only to raise funds but also to gauge customer interest and validate market demand.
- Gauge Interest in Social Media: Engage online communities to conduct polls and gather additional perspectives. This interaction provides a real-time sense of interest and expectations.
- Create a Pre-Launch Landing Page: Develop a landing page to capture email addresses and measure interest levels. This strategy helps in building a potential customer base before the product launch.
- Meet Customers in Person: Participate in local markets, craft shows, or relevant events to meet potential buyers in person and collect direct suggestions for refinement.
By systematically conducting these key validation steps, businesses can increase the chances of introducing a product that people genuinely want by focusing development around user feedback every step of the way. This helps ensure resources are invested to best satisfy an authentic need.
Strategies for Effective Product Validation
Engaging with Customers and Market Analysis
1. Low-fidelity Prototyping:
- Engage in low-fidelity prototyping to quickly uncover user needs and preferences. This method is effective in identifying missing features and potential improvements early in the development process.
2. Customer and Competitor Research:
- Conduct detailed customer research to gather insights directly from your target audience. This approach is crucial when prototyping or smoke testing is not feasible.
- Perform competitor research by analyzing competitors’ financial reports, social media activity, and staffing levels to gain a comprehensive understanding of the market landscape.
3. Utilizing Digital Tools for Feedback:
- Create smoke test landing pages to pre-sell the product and measure interest by monitoring traffic and conversion rates.
- Use social media polls and posts to collect feedback on product versions, names, features, or colors, providing quick and actionable insights.
Pre-Launch Strategies
1. Crowdfunding and Pre-orders:
- Start a crowdfunding campaign to assess market interest and gather funds before full-scale production. This strategy not only tests the market’s response but also helps in refining the product with backer feedback.
- Implement a pre-order system to validate market demand. Set a minimum number of orders required to go ahead with production, ensuring that there is sufficient interest before significant investment.
2. Interactive Customer Engagement:
- Develop a pre-launch landing page to capture email addresses and gauge interest levels. This setup serves as a preliminary indicator of market enthusiasm and helps in building a potential customer base.
- Organize events, such as prototype showcases or community engagement activities, to physically demonstrate the product and directly interact with potential customers. This face-to-face feedback is invaluable for immediate reactions and suggestions.
Analytical Approaches for Validation
1. Analyzing Digital Engagement:
- Monitor analytics on landing pages to understand user behavior, such as time on page, conversion rates, and interaction depth. These metrics are crucial for assessing the effectiveness of marketing efforts and the product’s appeal.
- Conduct email marketing campaigns to evaluate interest through metrics like newsletter sign-ups, open rates, and click-through rates. This data helps refine marketing strategies and understand customer engagement levels.
2. Market Demand Research:
- As previously stated, use tools like Google Trends and Ahrefs can be used to research existing demand and search volumes. This analysis provides insights into the market’s current interest levels and potential for new products.
- Gather and prioritize product feedback continuously to align product development with user expectations and market needs. This ongoing process ensures the product remains relevant and highly sought after.
By integrating these strategies, businesses can effectively validate their products, ensuring they meet market needs and have a viable path forward.
Leveraging Digital Tools for Product Validation
Digital tools provide valuable means for streamlining product validation in strategic ways. Tools allow testing and refining offerings in a more efficient manner prior to broad release.
An important technique is low-fidelity prototyping, permitting rapid assessments of whether solutions effectively tackle user problems. This provides important market data on factors like preferred attributes, fair pricing, and must-have elements.
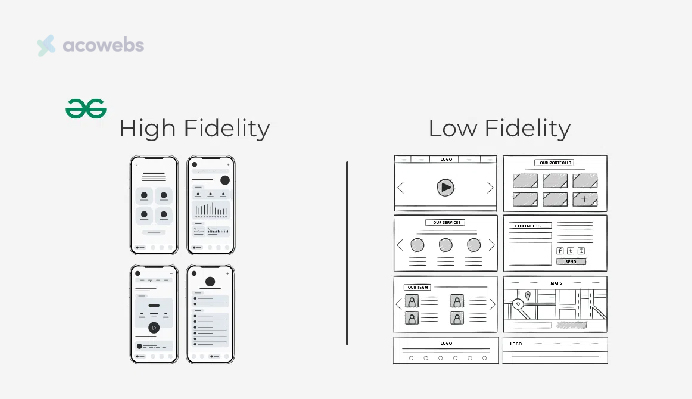
This approach is particularly beneficial in the early stages of development, where rapid iterations can significantly influence the final design and functionality of the product.
Another effective digital tool is the creation of smoke-test landing pages. These pages are set up before the actual software or product is fully built to pre-sell the idea and monitor traffic and conversion rates.

This strategy is crucial for gauging market interest and can prevent significant investment in products that may not meet consumer expectations. Additionally, companies often use pre-ordering systems where real pre-orders are collected for a new version of an existing product.
Setting a minimum number requirement helps businesses decide whether to proceed with the development, ensuring there is substantial demand before significant resources are allocated.
Moreover, digital tools extend to the realm of customer engagement and feedback collection. Platforms enabling remote user testing provide developers invaluable insights through video recordings, verbal feedback, and written responses, enabling observation of how individuals actually utilize products in real-time settings.
Digital analytics for websites present comprehensive behavior data, tracking user interactions and traffic sources plus conversion metrics, which are critical for understanding varying product versions’ effectiveness.
Furthermore, A/B testing tools facilitate experiments comparing minor alterations to design, characteristics, or material, letting teams refine solutions according to user responses.
These digital strategies, when combined, offer a robust framework for product validation, ensuring that products not only meet technical requirements but also resonate well with target audiences.
By leveraging these tools, companies can enhance their product development processes, increase market responsiveness, and ultimately launch products that are more likely to succeed.
Common Pitfalls in the Product Validation Process
In the journey of product validation, certain common pitfalls can significantly derail the effectiveness of the process. Recognizing and avoiding these pitfalls is crucial for ensuring that product validation efforts are successful and that the product truly meets market needs.
Overlooking Market Feedback

A significant pitfall during product validation comes from neglecting real user feedback. Businesses frequently depend excessively on their internal viewpoints and analytics rather than truly involving intended customers.
This disconnect risks creating a solution lacking features the market truly demands. It is paramount to build direct feedback avenues, like user experience testing and real-time feedback tools, to precisely capture consumer perspectives.
Only by earnestly listening to target audiences can businesses develop offerings addressing authentic needs that drive success. Omitting that input significantly dims chances of fulfilling what the market seeks, rather than what a company alone assumes it seeks.
Insufficient Testing Phases
Another frequent error is the inadequate testing of the product under diverse real-world scenarios.
Many businesses conduct limited tests that do not fully simulate the customer’s environment or overlook potential use cases. This can result in products that perform well under controlled conditions but fail to meet expectations under normal usage.
Expanding the testing phases to cover a broader range of conditions and incorporating stress tests can help identify and rectify these issues before the product goes to market.
Bias in Data Interpretation
Lastly, a common pitfall is the biased interpretation of validation data. Confirmation bias can lead teams to favor data that supports their preconceived notions about the product’s performance.
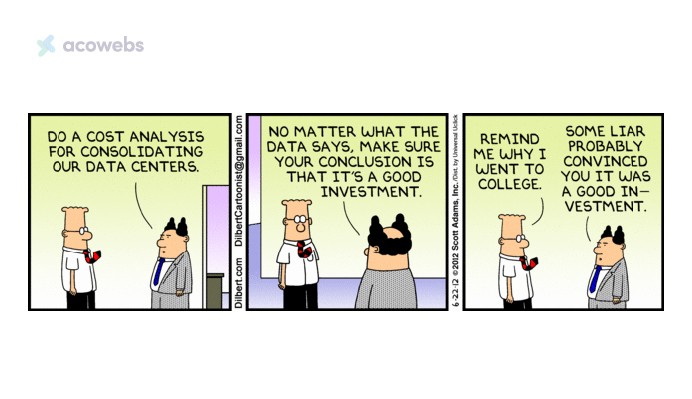
This bias can skew the development process and result in a product that does not effectively address the market’s needs.
It is crucial to establish a rigorous, objective framework for data analysis during the product validation process to ensure that decisions are data-driven and unbiased.
Case Studies: Successful Product Validation Examples
1. IMVU: Pioneering Social Connectivity
IMVU‘s inception as a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) showcased the power of early user engagement despite its initial technical imperfections. Developed over six months, the early version was bug-ridden yet sufficient to test the concept of network effects.
This strategic move paid off significantly as it led to a user base expansion, eventually reaching millions and generating approximately 50 million dollars in annual revenue by 2011.
2. Uber: Revolutionizing Urban Mobility
Uber began its journey as UberCabs, an MVP aimed at simplifying the process of hailing a taxi.
The initial app version, which was distributed through a unique code among a small user base, included basic features that allowed users to connect with cab drivers and handle payments via credit card.
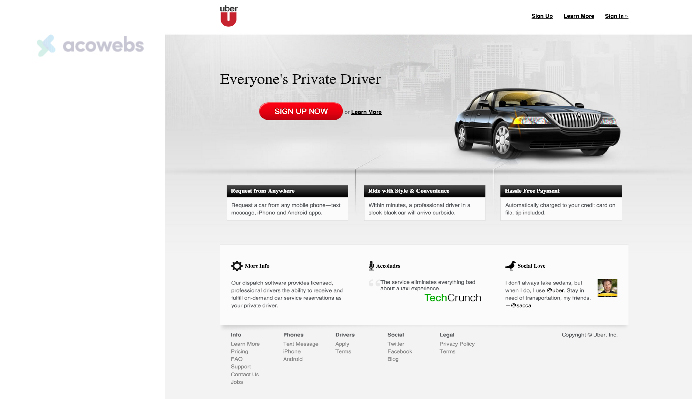
This MVP was crucial in validating the demand for such a service, leading to further developments and iterations based on user feedback. Today, Uber has transformed into a global leader in urban mobility.
3. Airbnb: Transforming the Travel Industry
Starting with a simple concept of offering air mattresses in a loft for conference attendees in San Francisco, Airbnb‘s founders quickly validated the market demand for unique, affordable lodging options.
This validation phase involved creating an MVP website that allowed them to test their assumptions and gather early user feedback.
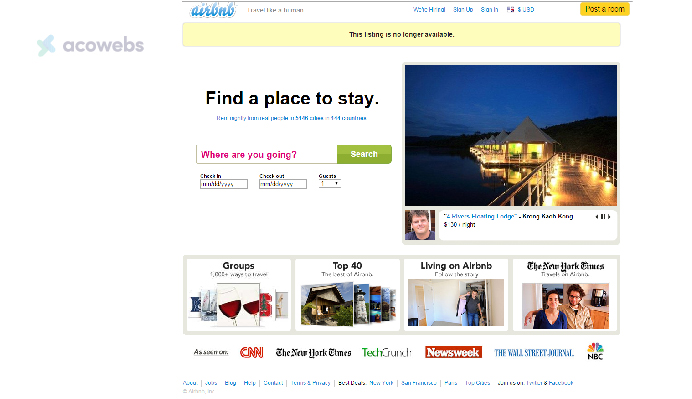
The success of this approach helped pivot their business model, leading to Airbnb’s expansion with listings in over 220 countries and reaching millions of users worldwide.
Conclusion
Through the exploration of product validation processes and strategies, it becomes evident that the path from a concept to a successful market offering is intricate yet achievable. The discussions reinforced the indispensable value of product validation in aligning products with market demands and customer expectations.
This endeavor not only mitigates risks associated with market entry but also strategically positions products to meet real user needs, thereby enhancing the likelihood of a product’s success.
The effectiveness of product validation, infused with rigorous testing, customer feedback, and a continuous improvement philosophy, underscores its role as a cornerstone in product development and market introduction processes.
As companies navigate the competitive and ever-evolving market landscape, adopting a strategic approach to product validation emerges as a critical factor in realizing product concepts that are both viable and effective in meeting the intended market and consumer requirements.
Acowebs are the developers of WooCommerce Dynamic Pricing the best way to add discounts based on a range of unconditional and considerable criterias to set with a sophisticated user interface which makes your efforts much easier. discount rules for woocommerce also comes with Percentage / Fixed price discounts.








 Login
Login
 Cart
Cart