The fast-growing demand for speedy product deliveries is driving innovation in last-mile logistics. New technologies like autonomous ground robots and drones show promise to meet this need. Where once conceptual, these systems are now delivering goods in certain areas.
Robot delivery vehicles can autonomously navigate sidewalks to drop off items. Drones provide an aerial approach, flying packages to destinations rapidly. Both options aim to revolutionize how companies fulfill orders and how customers receive them. By cutting out human drivers, they intend to offer faster, lower-cost, and more sustainable delivery over traditional methods.
However, widespread implementation faces barriers. Robots and drones must demonstrate safety and reliability at scale. Regulatory standards for drone deliveries are still evolving. If adopted, their impact could be transformative.
Businesses may gain new delivery capabilities and means to lower costs. Customers may benefit from deliveries made within hours of ordering. With the growth in quick commerce, these emerging technologies present an opportunity to reshape the industry.
Current State of Last-Mile Delivery

Getting packages into customers’ hands during the “last mile” of delivery, which involves transporting items from warehouses to homes or workplaces, has become a pivotal concern for logistics networks.
As online shopping continues exploding in popularity, the demand for smooth last-mile delivery has skyrocketed, severely straining workers who were already feeling overloaded.
This crucial part of the logistics industry confronts major challenges, as most shipping companies report that last-mile delivery poses the biggest challenge in the entire order-fulfillment process.
Inefficiencies in Traditional Methods
Traditional last-mile delivery methods have problems that increase costs and reduce customer satisfaction. The challenge is that deliveries are the most expensive and time-consuming part of the supply chain, costing up to 41% of shipping.
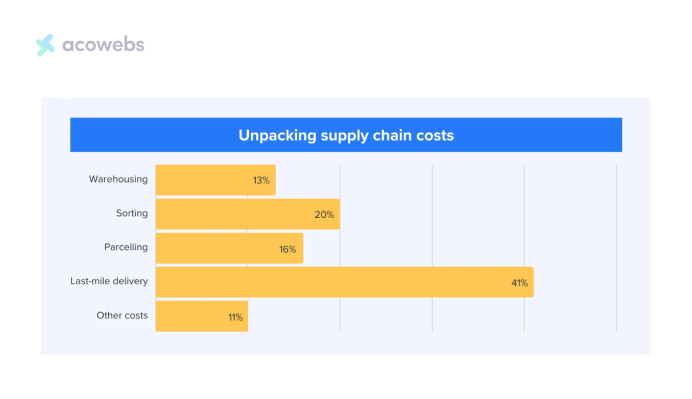
Key issues include poor tracking details, failed deliveries, inefficient routes, and no route optimization.
These problems often result in deliveries not happening on the first try, between 2% to 10% of the time. This costs more money and dissatisfies customers. It also increases carbon emissions due to rescheduled deliveries.
In order to fix these issues, businesses use systems that provide real-time information and optimized routes. This helps reduce delivery times, fuel use, and company expenses. Adopting such solutions can improve efficiency and sustainability while strengthening competitiveness in the important last-mile logistics industry.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of last-mile transportation is sizeable, contributing to more than a third of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in the logistics sector.
In the European Union, where road transit is ubiquitous, about three-quarters of the total greenhouse gases originate from road transport. Emphasis on faster deliveries regularly leads to inefficient practices, like transport vehicles leaving room for additional packages, resulting in greater carbon emissions.
To remedy these environmental concerns, companies are exploring alternative solutions. Out-of-home delivery, which consolidates multiple parcels at a single collection point, has exhibited the aptitude to reduce CO2 emissions by up to 58% compared to the traditional approach of only direct delivery in urban areas.
Additionally, transitioning to electric vehicles or cargo bikes for shipments can notably reduce the environmental footprint of last-mile activities. Adopting sustainable technologies and consolidation approaches can benefit both the climate and operating expenses.
Labor Shortages
The logistics industry, specifically the last-mile delivery segment, is grappling with considerable labor scarcity. These scarcities stem from diverse elements, like high turnover rates, an aging workforce, and increased demand for shipping services.
In North America, 37.8% of last-mile shipping companies reported obtaining qualified drivers as their most significant challenge.
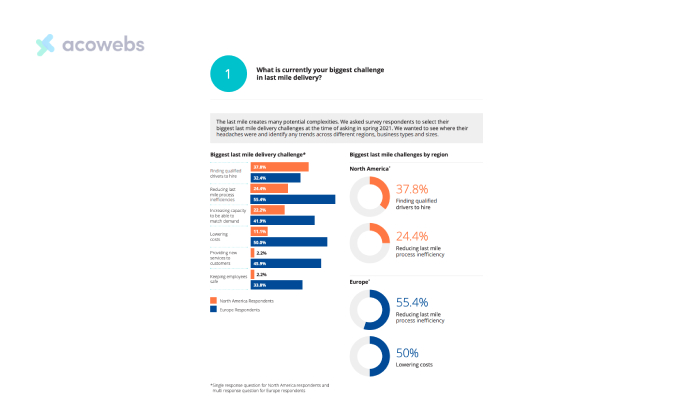
To battle this issue, enterprises are executing various strategies. These involve offering competitive compensation and advantages, investing in thorough training and development programs, and providing flexible schedules.
For example, Amazon has faced struggles in retaining delivery drivers and has implemented higher wages and extra benefits to attract and retain employees. Similarly, FedEx has increased wages and offered sign-on bonuses to attract new drivers.
As the last-mile delivery landscape continues evolving, addressing these difficulties will be crucial for businesses to meet e-commerce’s rising demands while minimizing environmental impacts and overcoming labor scarcity.
The Rise of Quick Commerce
Quick commerce, also called q-commerce, signifies the next stage of development in online shopping, focusing on extremely rapid delivery of goods to customers. This pioneering model pledges to provide items within an hour or even minutes after the placement of an order.
Unlike traditional e-commerce, which can take days to complete orders, q-commerce aims to offer nearly instant satisfaction to shoppers. This model is uniquely popular for necessary supplies like groceries, medicines, and everyday household items.
As consumer demands for speed and convenience persist and grow, quick commerce has surfaced as a profoundly transformative solution within the retail sector.
Consumer Demand for Rapid Delivery
The rise of quick commerce is propelled by the expanding desire for instant gratification in the digital era. As customers become accustomed to on-demand services across various spheres of life, they increasingly anticipate comparable immediacy in their shopping.
According to Statista, in 2023, Gen Z shoppers were most prepared to spend for two-hour delivery, typically parting with nine percent of the order total.
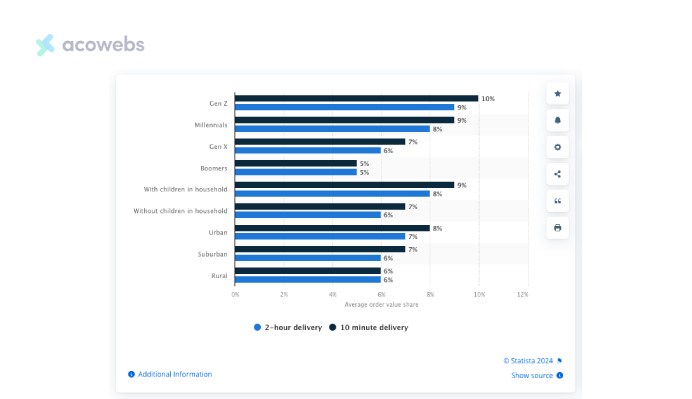
Millennials and customers with children living at home followed suit, each group normally willing to pay an average of eight percent of the order total for identical expedited shipping.
Challenges in Traditional Delivery Models
Traditional delivery methods face considerable challenges in fulfilling the demands of modern customers. As stated previously, the last-mile shipping problem, accounting for up to 41% of total transportation costs, has been an ongoing issue for e-commerce businesses.
Additionally, failed initial deliveries, which can extend from 2% to 10%, lead to increased expenses and dissatisfied customers.
In order to tackle these challenges, quick commerce relies on a network of local hubs or micro-fulfillment centers strategically situated near high-demand areas.
This approach allows companies to pick, pack, and deliver products rapidly, often using diverse delivery methods such as bicycle couriers and small vehicles to navigate urban environments smoothly.

As quick commerce continues evolving, it presents both opportunities and difficulties for retailers. While it offers a novel value proposition and potential for increased consumer loyalty, it also necessitates considerable investments in technology, infrastructure, and logistics to satisfy the requirements of swift transportation.
As we will explore in the next sections, companies are looking to cutting-edge solutions such as autonomous delivery robots and drones to further optimize speed and efficiency in quick commerce.
Robotic Delivery Solutions
Robot delivery solutions are emerging as a groundbreaking technology within the quick commerce sphere.
These self-governing machines are engineered to navigate urban roadways and transport packages to customers, providing a preview of the potential future of last-mile logistics.

Companies like Foodora have now started employing delivery robots in metropolitan districts, demonstrating the promise of this novel technique.
Autonomous Ground Robots
Autonomous delivery robots (ADRs) are small vehicles that operate on sidewalks without a human driver. They use various technologies like lasers, cameras, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to see and avoid obstacles as they navigate.
With a top speed around a brisk walking pace of 4 miles per hour, ADRs are designed to blend in smoothly with pedestrians in urban areas.
ADRs have shown potential in different test programs and rollouts. For example, Starship Technologies has expanded its fleet to over 2,000 zero-emissions delivery robots after completing more than 5 million deliveries worldwide.

Similarly, Serve Robotics has partnered with Uber Eats to put about 2,000 robots to work carrying loads up to 50 pounds across multiple U.S. cities.
The robots from both companies rely on their sensor suites and onboard computers to navigate autonomously on sidewalks and deliver food or packages without a human operator.
Advantages of Robot Delivery
The implementation of robot delivery solutions offers several potential benefits for quick commerce:
- Cost Efficiency: Studies suggest that ADRs can significantly reduce delivery costs. Hoffmann and Prause estimate that the cost per delivery using ADRs can be as low as 1 euro, which is 15 times less expensive than traditional delivery services.
- Time Savings: Autonomous deliveries are efficient with time, leading to increased cost-effectiveness. Optimizing distribution through ADRs can result in both time and cost savings.
- Environmental Impact: By reducing the number of delivery vehicles on the road, robot delivery solutions may help decrease traffic and air pollution in urban areas.
- Operational Flexibility: ADRs can operate around the clock, potentially improving delivery times and customer satisfaction.
- Accessibility: Robot delivery can increase accessibility to products in areas that are challenging to reach by traditional means.
While robotic delivery solutions show great potential, it’s important to note that they are intended to complement human delivery personnel rather than replace them entirely.
As this technology continues to evolve, it is poised to play an increasingly significant role in transforming quick commerce and last-mile delivery operations.
Drone Delivery Technology
Drone delivery technology is advancing quickly, providing a promising approach for last-mile logistics difficulties.
This innovative method involves using unmanned aerial vehicles to transport packages from retailers directly to customers, similar to how traditional courier services operate.

As the technology continues developing, it aims to lower costs while raising delivery effectiveness for various supply chain uses.
How Drone Delivery Works
Drone delivery networks ordinarily operate autonomously through the utilization of advanced technologies including artificial intelligence systems and precise GPS navigation capabilities.
These small to medium-sized unmanned aircraft reliably maintain constant altitudes while efficiently guiding package transport directly to recipients’ locations.
Primarily, drones ferry parcels from near distribution centers or retailers straight to customers’ doorsteps, bypassing congested roadway traffic and other logistic challenges faced by conventional ground-based distribution approaches.
Companies such as Wing have engineered comprehensive aerial delivery platforms designed to seamlessly integrate into existing logistics infrastructure.
These platforms offer application programming interfaces (APIs) and user interfaces that allow businesses to incorporate drone delivery functionality, including features for online package tracking and delivery route optimization analysis.
Proper coordination of autonomous drones guided by advanced systems thus demonstrates the potential to revolutionize last-mile fulfillment networks.
Advantages of Aerial Delivery
- Speed and Efficiency: Drones can significantly reduce delivery times by taking direct aerial routes and avoiding traffic jams. This is especially helpful in urban areas where traditional delivery struggles with delays.
- Cost-Effectiveness: According to research firm Gartner, using drones for parcel delivery costs 70% less than van delivery. Lower energy use and reduced labor account for lower costs.
- Environmental Benefits: Drones, typically powered by batteries, offer a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional delivery vehicles. One study by Hokey Min found drones can use up to 94% less energy per package compared to other vehicles for last-mile deliveries.
- Accessibility: Drones can reach remote or hard-to-access places like rural areas or regions with difficult terrain, where traditional delivery trucks face challenges.
- Contactless Delivery: In situations when minimal contact is preferred, such as health crises, drones enable safe, contactless delivery solutions.
As drone delivery technology continues advancing, it promises to reshape logistics, offering faster, more efficient, and eco-friendly solutions matching modern consumer demands.
Innovative Use Cases
With a foundation laid regarding robotic and drone-powered delivery systems employed in quick commerce, we can shift focus to exploring some innovative ways these technologies are being applied.
Healthcare and Medical Supplies
Drones show tremendous potential to transform healthcare systems worldwide, especially access in remote communities.
In nations like Rwanda and Ghana, medical drones have substantially improved supply chain networks, transporting critical supplies like vaccines, blood products, and other medical supplies to rural areas previously underserved.

The United Kingdom’s National Health Service made history in 2022 through the world’s first drone delivery of chemotherapy treatment to a patient.
In Sweden, researchers at the Karolinska Institute partnered with drone operator Everdrone and emergency responders in western parts of the country to study whether drones could expedite getting defibrillators to individuals experiencing cardiac arrest more promptly than ambulances alone.
Across 55 real-world cases, drones arrived on average over three minutes faster than ambulances for 67% of emergency situations, highlighting their ability to cut critical response times compared to traditional ground transportation.
Grocery and Food Delivery
Drone technology is poised to significantly impact the food delivery industry.
A global consumer survey conducted by McKinsey found that consumers are prepared to adopt advanced air mobility services. Grocery delivery surfaced as the most promising near-term use case, according to respondents who viewed drones as capable of instant delivery.
Several prominent retailers have launched drone delivery pilot programs as well, including Tesco, Amazon, and Walmart, demonstrating growing commercial support for this futuristic supply chain solution.
Manna, a drone delivery startup, is presently conducting the world’s largest trial of its technology in Galway, Ireland, where grocery orders are fulfilled via autonomous aerial vehicles.

Initiatives like this highlight the burgeoning real-world potential of drone-based services to revolutionize last-mile food and essential goods delivery.
Emergency Response Applications
Unmanned aerial vehicles have proven tremendously useful for disaster response efforts. They enable swift mobilization, connectivity to difficult terrain, and enhanced situational understanding for frontline workers.
Drones, outfitted with thermal sensors and cameras, efficiently detect individuals trapped in complex spaces like debris piles and underground during search and rescue missions.
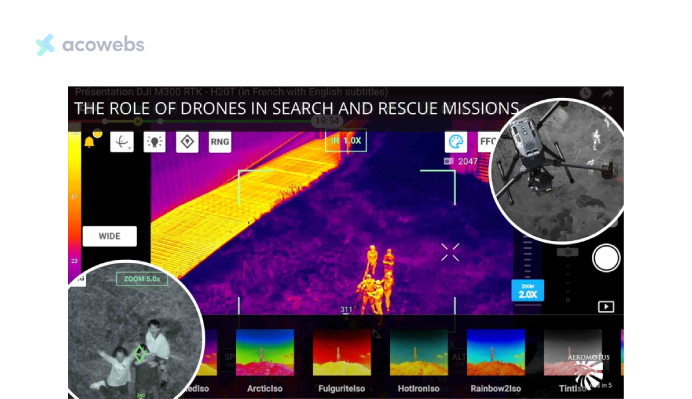
They also aid damage inspection duties, allowing for expedited and precise analysis of impacted localities.
In emergency scenarios, drones maintain the potential to deliver vital supplies such as medical equipment, food, and other necessities to locales that may otherwise be challenging or impractical to directly access.
Overall, robotic aviation continues to demonstrate clear value by intensifying response activities and improving outcomes when seconds and minutes count most during crises and natural disasters.
Challenges and Considerations
The implementation of robots and drones in quick commerce faces several hurdles. Regulatory challenges remain a significant obstacle, as many countries lack established rules for commercial drone usage.
Addressing airspace management, privacy concerns, and environmental impacts requires comprehensive legal frameworks.
Public acceptance is another crucial factor. Concerns over noise, privacy, and safety could impede adoption. Clear communication about operations and benefits, alongside stringent safety measures, is essential to build trust.
Technical malfunctions, such as robots and drones dropping items at incorrect addresses or damaging goods during delivery, further contribute to public skepticism.
Infrastructure limitations also pose challenges. Widespread drone delivery requires robust physical and economic infrastructure, including designated take-off/landing zones, maintenance facilities, and advanced traffic management systems. This necessitates substantial capital investment.
Companies and private investors have begun exploring these infrastructure assets, but questions about their necessity persist, given the uncertain timeline for the widespread availability of delivery drones.
Conclusion
The emerging technologies of robotics and drone delivery show tremendous potential to transform last-mile logistics and quick commerce.
By automating the ‘last mile’ of transportation through autonomous ground vehicles and aerial drones, companies can provide customers with unprecedented speed and convenience by delivering goods within mere hours of ordering.
While implementation challenges around regulation, infrastructure, and public acceptance remain, real-world use cases demonstrate the viability and value of these innovative solutions. From healthcare access in remote areas to emergency response missions, robotic and drone-based delivery are creating new possibilities that could redefine supply chain networks.
As both the technologies and our acceptance of them continue to advance, quick commerce looks set to disrupt traditional models of retail and fulfillment. It will be intriguing to see how businesses, communities and customers stand to benefit from this rapidly emerging trend in the years ahead.
Acowebs are the developers of the WooCommerce Product Labels which let customers include custom product labels or product badges for the WooCommerce products.WooCommerce sales badges plugin provides you with different label styles and customizations for labels. It offers a easy-to-use UI to add labels to the selected products or categories.









 Login
Login
 Cart
Cart