Brands and consumers have formed a different relationship over the last decade due to the impact of technology. The automated customer service chatbot trend, influencer marketing, and other similar developments have now reached a new level in synthetic influencer storefronts.
AI avatars are ultra-realistic virtual characters that are deployed in digital shopping environments. They help customers choose products while engaging in human-like conversations.
The idea gained momentum in the late 2010s. Firms began looking at how AI could perform as well as social media stars. Brands such as Dior and Puma are deploying AI avatars, not just as models of clothing, but to recommend products and drive conversions.
The history of this idea originates from retail automation and the rise of social media influencers. Before online shopping, companies only uploaded static images and some product details. Soon enough, they realized human influencers can attract buyers.
As companies look for scalable, data-driven, and always-on options, synthetic influencers’ storefronts are the new ‘must-have’ in retail. Let’s see how.
Understanding Synthetic Influencer Storefronts
The avatars are not just animated figures; they’re powered by sophisticated algorithms, ML models, and natural language processing (NLP) systems. NLP allows the avatars to understand, react, and even adapt to customer behavior in real time.
As influencer marketing became more expensive and technologies around AI matured, businesses started thinking: What if we could create our very own influencer, who won’t get tired, always on brand, and works 24/7? That’s how synthetic storefronts started to develop.
These digital environments exist on websites, mobile apps, and even certain social media platforms, allowing customers to interact with AI avatars that provide product recommendations, answer questions, and simulate the experience of live shopping assistance.
The Role of AI Avatars in Digital Commerce
In a 2024 study published on ResearchGate, researchers found that virtual influencers significantly boost consumer purchase intention, especially when brand familiarity and product involvement are high. Effectiveness increases further when the influencer’s style aligns with audience expectations.
1. AI-Generated Personalities as Brand Ambassadors
Unlike traditional influencers, AI-generated characters are fully programmable; brands can shape them to embody specific values, styles, and messaging.
These avatar A.I.s, meanwhile, don’t age, flub lines, embarrass themselves, or post off-brand material. Rather, they are pure marketing, and they never stray from marketing’s goals, which is precisely why they are such perfect ambassadors long term.
Companies like LVMH, Calvin Klein, and Balmain have already sunk money into the virtual influencer storefronts, where the computer-generated faces share new collections, lead digital campaigns, and attend metaverse-based retail events.
The most successful avatars are given backstories, values, and personalities to enhance authenticity. Take Shudu, a high-fashion AI model developed by The Diigitals, or Imma, a Japanese virtual influencer known for her distinct pink bob and streetwear fashion, both are now mainstays in digital advertising.

Their appeal lies not just in novelty but in performance. According to a 2023 report by Influencer Marketing Hub, AI avatars can generate up to 3x higher engagement rates than traditional influencers in some campaigns, particularly among Gen Z audiences who crave innovation and diversity in content.
2. Real-Time Customer Interaction Through Avatars
The defining feature that sets AI avatars apart from other automated retail technologies is their capability to interact in real-time. Because of variations in NLP and large language models, avatars are able to engage in fluid conversations hampered by tone and intent and change responses accordingly.
This means that customers may “chat” with a realistic virtual associate who can direct them to different items in the inventory, explain product characteristics, and even recommend complementary products.
Retailers such as Alibaba and JD.com have already employed avatars on livestream shopping channels, where they act as digital presenters to host Q&As and respond to individual comments.
For instance, Alibaba’s Tmall featured a virtual host named Dong Dong, an AI-generated avatar developed for the 2022 Winter Olympics. She engaged with viewers in real time, answered questions about featured products, and even commented on sports highlights.
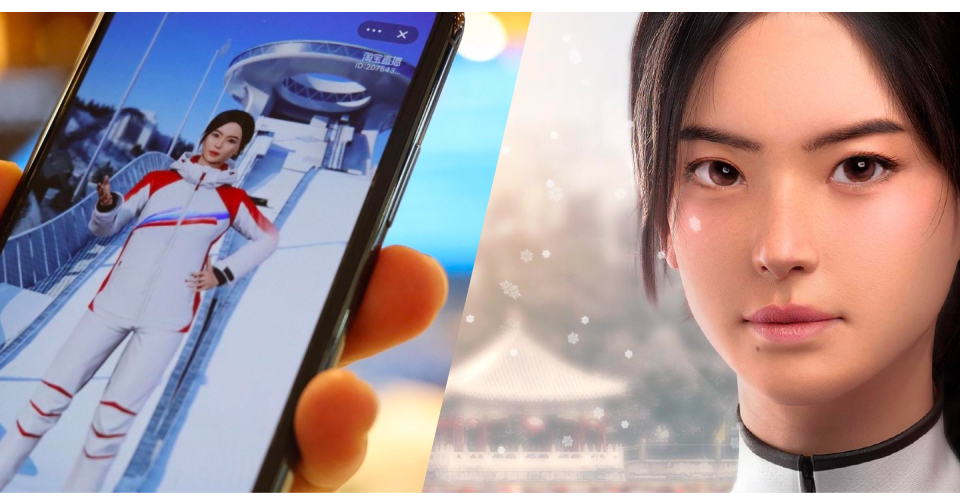

Shoppers get to trust you more. Understanding why consumers do not complete purchases on websites is not easy; it is, however, an opportunity to increase sales and reduce cart abandonment.
3. Customization and Product Recommendations
For a long time, personalization has remained a key pillar of effective digital commerce, and now AI avatars have brought it to life with a visual, interactive experience. By analyzing users’ beliefs, preferences, and past shopping behavior, these avatars can deliver real-time, personalized product recommendations.
For example, if one user spends an inordinate amount of time looking at eco-friendly skincare, the avatar might suggest a bundle or tell them there’s a discount coming up. We see results from these hyper-personalized experiences.
More importantly, AI avatars can refine recommendations over time, learning from each customer interaction to improve future responses. They offer a digital experience that feels increasingly “human,” without the inconsistencies or limitations of actual human sales associates.
Advantages of Using Synthetic Influencers as Sales Associates
The emergence of synthetic influencer storefronts has given brands a powerful alternative to traditional sales and marketing strategies. The advantages include:
1. Around-the-Clock Availability
Unlike human sales associates who require rest, holidays, or shift rotations, AI avatars operate without pause. This also guarantees that brands can continue serving customers around the world, regardless of time zones or shopping habits.
In 2020, Ralph Lauren launched a virtual store experience that digitally recreated its flagship store on Madison Avenue, New York. Shoppers could “walk through” the store using 3D navigation and interact with a virtual shopping assistant powered by AI.
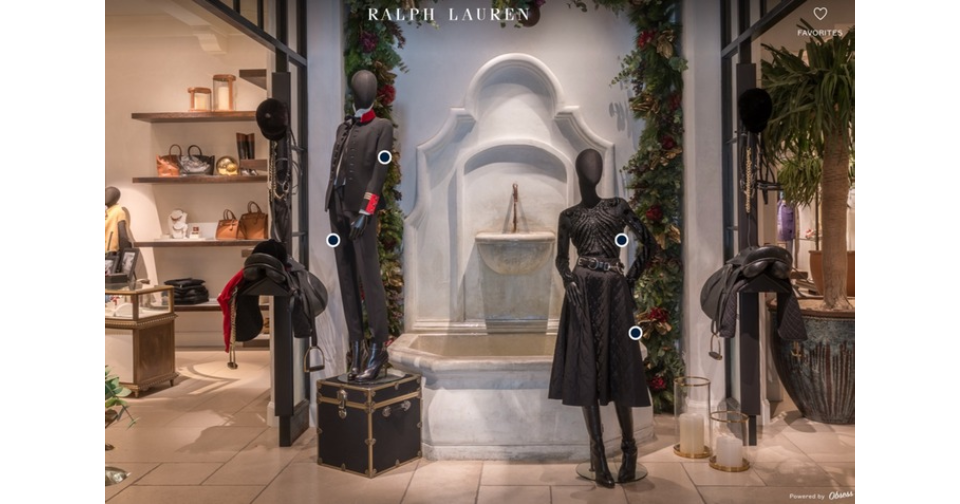

This assistant could answer questions about products, suggest outfit combinations, and even help with sizing. The immersive showroom was available on the brand’s website 24/7, where customers could browse through curated collections like the Polo Ralph Lauren line or the Purple Label.
It provided a boutique experience in a luxurious, digitally rendered space even when a store wasn’t open for business. Synthetic influencers, by existing continuously, make shopping easier, whether for international customers or late-night browsing.
2. Scalable Global Outreach
Scalability is one of the most practical benefits of AI-driven sales associates. Whether a brand is catering to ten customers or ten million, AI avatars can handle the load with ease. They don’t burn out, require training, or demand a salary increase when business grows.
Take H&M’s collaboration with virtual influencer Kuki AI. The avatar has appeared in promotional campaigns across multiple platforms and languages, instantly adapting to different cultural contexts. This allows the brand to speak to diverse audiences while maintaining a unified voice.

Such scalability helps companies reduce operational costs and avoid logistical challenges that come with hiring and managing a large human team across multiple regions.
3. Full Control Over Brand Messaging
One of the key issues with traditional influencers is unpredictability. Real people have opinions, can make mistakes, and may shift directions based on their own personal goals. AI avatars, however, are completely programmable and operate within clear, predefined parameters.
Shudu has represented brands like Fenty Beauty and Balmain, delivering brand-approved content without risk of controversy. Every post, pose, and interaction is scripted to align perfectly with the campaign’s objectives.
This level of control ensures brand messaging stays consistent, eliminating the PR risks that often come with human ambassadors.
4. Enhanced Customer Engagement Through Storytelling
Synthetic influencer storefronts offer something that basic websites or dumb chatbots cannot provide: immersive digital storytelling. AI avatars can get distinct personalities and backstories, making them relatable characters that consumers can emotionally connect with.
A great example is Imma, a Japanese AI avatar who models fashion and lifestyle brands. IKEA Japan had cast her to advertise IKEA’s furniture, showing her resting in her branded virtual apartment, chatting about her favourite pieces and how they fit into her digital life.
The biblical content was not so much a sales presentation as it was a way to make the case about product features. Through avatars like Imma, brands can transform product showcases into immersive experiences, fostering deeper customer loyalty and enhanced recall.
5. Personalization Without Human Error
The modern consumer expects personalized recommendations, but human agents can only do so much. Algorithms in AI avatars recognize conduct in real-time and offer customized suggestions aimed at improving the digital experience.
More often than not, these avatars use browsing history, preferences, and even emotional cues in conversation. A good example is Sephora’s virtual beauty advisor, an AI avatar designed to assist customers with skincare and makeup.
It helps customers find products according to their needs. Unlike the store associate in the traditional store, the avatar remembers preferences from previous visits so as to refine future recommendations.
Such personalisation improves sales advice and user satisfaction. The customer feels understood and appreciated, without jeopardizing the consistency impacted by human emotions, memory, or distraction.
Ethical and Technical Considerations
As synthetic influencer storefronts become more common, they also raise a few eyebrows. Just because we can replace human interaction with AI doesn’t always mean we should, at least not without thinking through the ethical and technical implications.
1. Transparency and Consumer Trust
Customers, especially those who shop online, desire openness. Additionally, it could appear dishonest if someone thinks they are speaking with a human and then discovers it was a machine.
Companies should disclose that algorithms, not humans, are used to construct these avatars. There is a lot that transparency can do to boost confidence.
In the same way that you wouldn’t mislabel a product, an AI avatar that makes false claims about itself could eventually face criticism or, worse, legal issues.
2. Deepfake Concerns and Misuse Risks
When avatars appear to be hyperreal, the difference between genuine and artificial becomes increasingly blurred. This leaves the potential for it to be abused, particularly when unauthorized avatars are generated from people’s likenesses or when AI-generated influencers are harnessed in deceptive advertising.
Brands must invest in ethical guardrails and secure tech if their avatars are not to end up being part of the problem. It’s not just innovation, it’s also accountability.
3. Data Privacy and Surveillance Concerns
AI avatars urgently need to process real-time data to accommodate personal recommendations. The data is often sensitive, though: user preferences, emotional cues, and behavioral habits.
Mishandling or leaks of such data can constitute a violation of consumer privacy rights, and it can result in a violation of compliance mandates such as GDPR or CCPA.
Brands must make sure they are combating data encryption, anonymization, and secure storage processes. Consumers should also have clear opt-in options and a choice of how their data is collected, maintained, and shared.
4. Algorithmic Bias and Representation Issues
Since synthetic influencers are data-driven, they can inadvertently perpetuate the kinds of societal biases that are reflected by that data.
For example, avatars may espouse certain beauty ideals, dialects, or shopping habits, and therefore exclude or misrepresent segments of the population.
It is essential to guarantee an inclusive representation in the design and training sets of avatars. Brands should work with ethicists, DEI experts, and multicultural teams to build avatars that reflect more people of different genders, races, ages, and abilities, rather than stereotyping them.
5. Dependency and Dehumanization
An over-reliance on AI avatars for customer engagement can risk dehumanizing retail experiences. While avatars can replicate many human traits, they can’t provide the same empathy, emotional intelligence, or ethical judgment that human sales associates offer, especially in sensitive or complex scenarios.
This raises concerns about job displacement and the loss of authentic interpersonal connections in commerce.
Retailers must consider hybrid interaction models that balance AI efficiency with human oversight, ensuring customers always have the option to escalate to a real person when needed.
The Future of Human vs AI Sales Roles
Will AI replace human sales associates entirely? Probably not, but it will change the game. We’re likely to see more hybrid models where AI handles routine queries and data-driven recommendations, while humans step in for complex needs, emotional nuance, or high-touch service.
Instead of thinking in terms of replacement, the future will be about collaboration, where human creativity and empathy are enhanced by AI’s speed and scalability.
The Future of AI-Driven Storefronts
As synthetic influencer storefronts continue evolving, what comes next might feel like science fiction but it’s already in motion. The next wave will be even more immersive, personalized, and interconnected.
1. Integration with AR/VR and the Metaverse
Imagine walking through a digital boutique wearing VR goggles or exploring a 3D showroom on your phone, with an AI avatar guiding you through outfits or gadgets. That’s the future.
As augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies improve, brands are merging these experiences with AI avatars to create fully interactive shopping spaces. Think of it as window shopping in the metaverse, with a personal stylist who knows you inside out.
2. Hyper-Personalized Shopping Experiences
What we’re seeing now is just the beginning. In the near future, AI avatars could greet you by name, remember your last purchase, and instantly suggest new items based on your lifestyle, values, or mood.
These interactions won’t just be helpful, they’ll feel deeply personal. For brands, this level of hyper-personalization means stronger customer loyalty and higher lifetime value. For consumers, it means shopping that feels like it “gets” them.
Measuring Success: KPIs and Analytics for Synthetic Storefronts
1. Engagement Metrics
One of the most immediate signs of success is how users engage with the AI avatar. This includes:
- Session duration: Are shoppers spending more time exploring the store with the avatar’s assistance?
- Interaction rate: How many customers initiate a conversation with the avatar? What is the drop-off rate during interactions?
- Repeat engagement: Do users return to interact with the avatar again, indicating trust and utility?
2. Conversion and Sales Impact
Ultimately, synthetic storefronts should lead to improved conversion metrics:
- Click-through rates (CTRs) from avatar recommendations.
- Cart completion rates for avatar-assisted sessions versus non-assisted sessions.
- Average order value (AOV) in AI-assisted transactions.
- Upsell/cross-sell effectiveness, such as the number of complementary items added based on avatar suggestions.
Tracking these helps businesses measure direct sales impact and ROI.
3. Personalization Accuracy
AI avatars thrive on tailoring recommendations, but how well are they doing it? Useful metrics include:
- Recommendation acceptance rate: How often do customers choose items suggested by the avatar?
- Personalization match score: Does the suggested item align with the user’s preferences, history, or behavior?
- Feedback and rating systems: Are users giving thumbs up/down or leaving qualitative feedback on avatar interactions?
These insights help refine the avatar’s algorithm and improve future engagement.
4. Customer Satisfaction and Trust
Since avatars simulate human interaction, emotional response matters:
- CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score) and NPS (Net Promoter Score) are specific to avatar interactions.
- Sentiment analysis of conversations (via natural language processing) to gauge tone satisfaction.
Conclusion
Synthetic influencer storefronts are redefining the way we shop. Powered by AI, these digital avatars act as tireless, brand-aligned sales associates, offering personalized, interactive experiences 24/7.
From luxury brands to fast fashion, companies are embracing this scalable, data-driven approach to boost engagement and sales. But with innovation comes responsibility.
Transparency, ethical AI use, and inclusivity must guide this transformation. As AR and VR evolve, these avatars will only grow more lifelike and intuitive.
Still, it’s not about replacing humans, it’s about enhancing retail with smarter tools. The future of shopping is both personal and digital, and synthetic influencers are leading the way.
Acowebs are the developers of Woocommerce Custom Product Addons which is a optimized, lightweight, and fruitful plugin that is simply the best to add extra product options using its custom form builder easily. WooCommerce custom fields also comes with drag and drop form builder, 22+ field types and custom price formula. WordPress offload media plugin which allows you to offload your media to cloud storage such as Amazon s3, Cloudflare r3, Google Cloud, Digital Ocean and more.









 Login
Login
 Cart
Cart