In an era of unprecedented global connectivity, the realm of commerce knows no bounds. The evolution of cross-border eCommerce has been nothing short of remarkable.
Just a few decades ago, international trade was primarily the domain of established, large-scale enterprises due to the formidable barriers presented by geography, trade restrictions, and the lack of digital infrastructure.
However, in a relatively short span of time, the digital revolution and advances in logistics have democratized global trade, enabling businesses of all sizes to participate in cross-border commerce.
The internet and the advent of secure online payment systems have turned the world into a vast marketplace accessible to anyone with a computer or smartphone. But, as the global cross-border eCommerce industry has flourished, it has also presented a new set of challenges.
The world of cross-border eCommerce is a complex web of regulations, logistical intricacies, and diverse consumer expectations. Let’s explore it to understand it better.
What is Cross-Border eCommerce?
Cross-border eCommerce, international eCommerce, or global eCommerce is purchasing and selling products and services online between entities or individuals in different countries.
This practice involves digital transactions that cross international borders, enabling businesses and consumers to engage in a global marketplace without necessitating a physical presence in a foreign country.
Its rise can be attributed to the growth of the internet, the adoption of digital payment systems, and the streamlining of international shipping and logistics.
This phenomenon empowers businesses to extend their customer base beyond their domestic borders, granting consumers access to a more extensive array of products and services from various parts of the world.
According to the latest findings, there is a high probability that the total value of global cross-border eCommerce will exceed a staggering $1 trillion in 2023.
Key Features of Cross-Border eCommerce
This globalized digital marketplace presents several key features that distinguish it from domestic eCommerce. They include:
1. Global Access
Cross-border eCommerce offers businesses the ability to reach a worldwide customer base. Unlike domestic eCommerce, which primarily caters to a single national market, cross-border eCommerce allows businesses to access consumers in multiple countries.
This global reach expands their market potential, offering new markets and revenue streams that may not be available in their home country. It enables businesses to tap into diverse customer demographics and preferences, increasing their growth prospects and revenue opportunities.
Amazon started as an online bookstore in the United States but quickly expanded its operations to become a global eCommerce giant. Today, Amazon operates in over 180 countries, providing access to a vast and diverse range of products for customers around the world.
For instance, a customer in India can browse and purchase a book, electronic device, or fashion item directly from Amazon’s website or app.
The product is then shipped from an Amazon warehouse in the United States, the United Kingdom, or another country, making it accessible to the Indian customer.
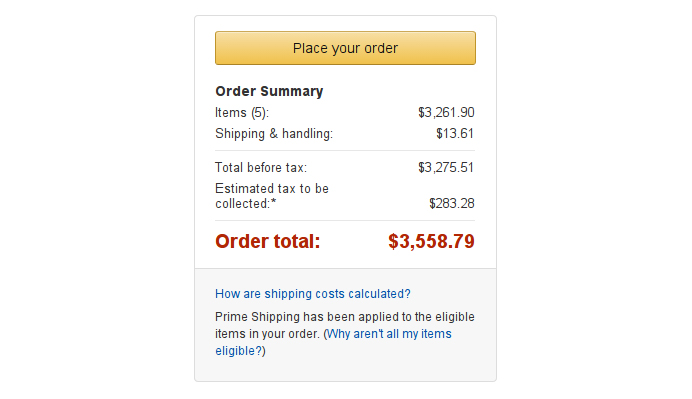
2. Currency Conversion
Cross-border eCommerce platforms streamline international transactions by offering currency conversion services. These platforms cater to a diverse global customer base, enabling buyers and sellers to interact seamlessly in their preferred local currencies.
When a buyer from one country wishes to purchase a product listed by a seller in another, the platform intervenes by converting the purchase price into the buyer’s currency, usually at competitive exchange rates.
This process simplifies the shopping experience, as customers can grasp the cost without needing to convert and compare prices manually.
Simultaneously, sellers benefit from a broader customer reach, as complex currency conversions don’t deter potential buyers. This service mitigates the risks associated with fluctuating exchange rates and fosters trust in cross-border transactions.
3. International Shipping
International shipping and logistics networks have undergone significant enhancements, resulting in a notable transformation of how products are transported across borders.
One key aspect of this transformation is the optimization of shipping routes and methods, which has led to reduced transit times and lower shipping costs.
Advanced tracking and tracing systems now provide real-time monitoring of shipments, offering sellers and buyers visibility into the movement of their products.
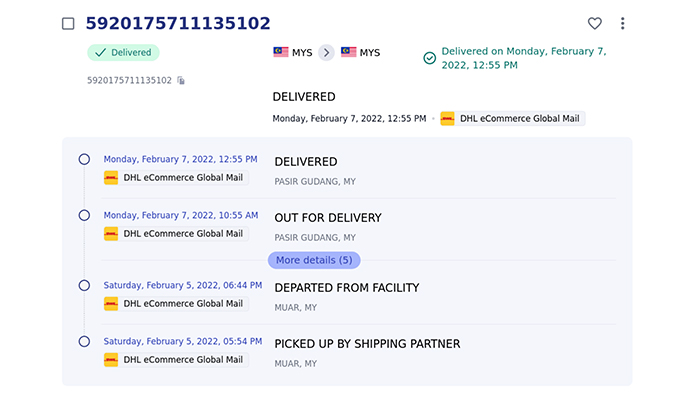
The diversification of international shipping services has given customers a range of options, including express delivery, standard shipping, and eco-friendly alternatives, making it easier for buyers to select shipping methods that suit their preferences and budgets.
Moreover, streamlined customs clearance processes have reduced delays and simplified regulatory procedures, resulting in a smoother experience for those engaged in cross-border trade.
4. Regulatory and Tax Considerations
Businesses involved in cross-border eCommerce face a complex web of regulatory and tax considerations. International trade regulations and customs duties play a pivotal role in the movement of goods between countries.
Compliance with these regulations is essential to ensure smooth operations. Businesses need to be well-versed in import and export rules, as well as product-specific restrictions and requirements, to avoid costly delays or legal issues.
Additionally, tax implications are a significant concern. Companies must understand and manage various taxes, including value-added tax (VAT), customs duties, and income tax.
5. Localization
This means going beyond mere language translation; it entails a deep understanding of local customs, behaviors, and market nuances.
Localization is a critical strategy in achieving success in cross-border eCommerce. It involves tailoring the entire shopping experience to resonate with the cultural and linguistic preferences of target markets.
Website localization is essential, as it ensures that the website is not only available in the local language but also considers factors like date formats, currency symbols, and culturally relevant imagery. This creates a more inviting and relatable shopping environment.
Localized marketing efforts are equally vital. Adapting advertisements, promotions, and content to align with local holidays, traditions, and consumer interests enhances the appeal of products and services.
Additionally, providing customer support in the local language and during convenient time zones establishes trust and fosters a sense of accessibility.
6. Import and Export Regulations
Businesses engaged in cross-border eCommerce must adhere to import and export regulations of both the source and target countries to ensure lawful and efficient international trade operations.
Import regulations involve compliance with the rules and requirements imposed by the destination country for products entering its market.
These regulations encompass product standards, safety certifications, labeling, and customs documentation. Failure to meet these criteria can lead to delays, fines, or even product confiscation.
On the other hand, export regulations encompass the rules and restrictions set by the country of origin on goods leaving its jurisdiction.
These rules can include export licenses, restrictions on certain products, and compliance with international trade agreements. Violating export regulations can result in legal consequences and damage a business’s reputation.
Challenges Facing Cross-border eCommerce and The Solutions
Cross-border eCommerce comes with a unique set of challenges that must be navigated effectively to unlock its full potential. They include:
1. Regulatory Hurdles
Cross-border eCommerce encounters a significant obstacle in the form of regulatory hurdles, which encompass customs, taxes, and trade agreements. These challenges are multi-faceted and can have a profound impact on the operations and success of businesses engaged in international trade.
They manifest as complex, often differing rules and requirements that companies must navigate when moving goods across borders. This slows down the shipping process and also results in increased operational costs, all of which collectively create substantial barriers to market entry for businesses looking to expand their reach into global markets.
For example, consider a small eCommerce company based in the United States that wishes to sell its products to customers in the European Union (EU). The regulatory hurdles begin with customs procedures, which demand meticulous documentation and adherence to specific requirements for each product.
These requirements may differ from those in the U.S., and the company must ensure that every shipment complies with the EU’s customs rules. Additionally, the challenge extends to tax regulations.
The EU has a complex Value Added Tax (VAT) system that varies from one member country to another.
The eCommerce business must not only understand these variations but also ensure that it correctly charges, collects, and remits VAT, which can be particularly intricate when selling digital goods or services.
Furthermore, trade agreements come into play. The U.S. and the EU have distinct trade agreements that impact the terms of import and export.
The eCommerce company must comprehend the specific provisions and requirements set forth in these agreements to ensure that its goods can be freely traded between these two regions.
To address these regulatory hurdles, the company may engage in collaborative advocacy and compliance efforts.
This involves working with industry associations, governmental bodies, and international organizations to advocate for simplified, standardized, and harmonized regulations that govern cross-border trade.
2. Language and Cultural Barriers
Language disparities and cultural nuances present significant obstacles in the realm of cross-border eCommerce, profoundly impacting the overall customer experience. The challenge becomes evident when a company attempts to enter a foreign market without addressing these barriers adequately.
Consider a scenario where a US-based eCommerce business expands its operations to target the Chinese market. The website, product descriptions, and customer support are primarily in English, causing issues for potential Chinese customers who may not be proficient in the language.
Navigating the website becomes a challenge, as does understanding product details, leading to a lack of trust and hesitancy in making purchases. Moreover, the company’s marketing campaigns, rooted in Western cultural references, can unintentionally convey messages that are culturally inappropriate or irrelevant to the Chinese audience.
The solution to these issues is multifaceted. eCommerce businesses must offer multilingual customer support to cater to the language preferences of their target market. Translating product descriptions and ensuring they are culturally relevant is paramount.
Market research is crucial to understanding consumer behavior and preferences in the target market, ensuring that marketing messages, imagery, and branding resonate with the local audience.
3. Returns and Refunds
Handling returns and refunds involves navigating a web of differing regulations, shipping costs, and customs procedures, making the process less straightforward than domestic returns.
For customers, this complexity can lead to dissatisfaction when attempting to return or exchange products, while for businesses, it can result in increased operational costs and administrative burdens.
To address these challenges effectively, businesses should start by clearly communicating their return policies to customers, ensuring they understand the procedures and requirements for returning items.
Establishing return centers in key international markets can help streamline the process, making it more efficient and cost-effective for both the customer and the business. Also, the adoption of technology solutions designed for cross-border returns can simplify the entire return process, providing guidance and automation to ensure compliance with specific regulatory requirements.
4. Tariffs and Trade Barriers
Tariffs are taxes or duties imposed on imported or exported goods, often as a means of protecting domestic industries, regulating trade, or generating revenue. When trade tensions arise, they can result in the imposition of tariffs, affecting cross-border eCommerce operations in several ways.
Tariffs increase the cost of imported goods. This can have a significant impact on product pricing. For example, a business sourcing electronic components from another country may see a sudden increase in the cost of these components due to newly imposed tariffs.
To maintain profitability, they may need to raise prices for consumers, potentially making their products less competitive in the market. Alternatively, the business might absorb the additional costs, which can affect its overall profitability.
Trade tensions and tariffs can lead to uncertainty and unpredictability in the cross-border trade landscape. Companies may find it challenging to anticipate changes in trade policies and the associated cost implications. This unpredictability can make it difficult to plan and manage the supply chain effectively, affecting product availability and delivery times.
Diversifying sourcing by exploring alternative suppliers and regions with favorable trade agreements can reduce reliance on a single source and mitigate the impact of tariffs. Additionally, continuous market analysis is crucial for staying informed about trade developments and trends.
5. Currency Fluctuations
Currency fluctuations refer to the changes in the value of one currency relative to another. In cross-border eCommerce, businesses often engage in transactions involving multiple currencies. These fluctuations can affect several aspects of the business.
Pricing may become inconsistent and less predictable as exchange rate shifts can alter the cost of goods in foreign markets. For example, a U.S.-based eCommerce company selling products in euros may see its product prices fluctuate due to changes in the EUR/USD exchange rate. Such pricing variability can confuse and deter customers.
Profitability is directly affected when exchange rates move unfavorably. If a business buys goods in one currency and sells them in another, unfavorable exchange rate movements can reduce profit margins or even result in losses. For instance, a company purchasing electronics from Japan in Japanese yen might face reduced profits if the yen strengthens against their local currency.
Inconsistent or unexpected changes in prices can erode customer confidence, as they may perceive it as unfair or unreliable pricing. To address these challenges, cross-border eCommerce businesses can implement currency risk management strategies.
Currency risk management includes measures such as hedging, which allows businesses to protect themselves against adverse exchange rate movements.
6. Competitive Challenges and Market Saturation
Cross-border eCommerce faces a dual challenge: fierce global competition and potential market saturation in some regions. The competition is intense, and it can be daunting for businesses to stand out among a multitude of international competitors.
This challenge is exemplified by the scenario where an eCommerce company seeks to expand into a market that’s already inundated with competitors offering similar products or services. In such an environment, simply entering the market and expecting to thrive is a considerable challenge. The overarching competitive landscape of cross-border eCommerce further compounds this.
The solution to these intertwined challenges is twofold. Firstly, businesses must focus on differentiation and in-depth market research. This entails developing unique selling propositions that set them apart from competitors and, importantly, conducting thorough market research to understand the nuanced preferences of customers in each region.
By tailoring marketing strategies and product offerings to align with the specific needs and desires of each market, businesses can create a competitive edge.
In cases where market saturation is particularly pronounced, niche targeting becomes paramount. Businesses must identify underserved segments or niche markets within the saturated space.
Conclusion
Cross-border eCommerce has experienced tremendous growth and transformation in recent years, opening up new opportunities for businesses to expand their reach. However, this expansion is not without its challenges.
Regulatory hurdles, language and cultural barriers, returns and refunds, tariffs and trade barriers, currency fluctuations, and competitive challenges are some of the key obstacles that businesses need to navigate effectively.
To overcome these challenges, businesses must adopt a proactive approach, utilizing technology solutions, engaging in collaborative advocacy, and adopting strategies to localize their operations.
This includes offering multilingual customer support, translating and culturally adapting product descriptions, establishing return centers in key international markets, diversifying sourcing, and implementing currency risk management strategies.
Furthermore, businesses need to differentiate themselves through unique selling propositions and conduct thorough market research to understand the preferences of customers in each target market.
Niche targeting within saturated markets can also provide a competitive advantage. Businesses that embrace these developments will be in a better fighting position.
Acowebs are the developers of the WooCommerce PDF Invoices and Packing Slips which generate PDF invoices automatically and add them to the confirmation emails sent to your customers. WooCommerce invoice plugin allow youCreate, edit, and modify your own templates and to download or print invoices and packing slips from the WooCommerce admin.









 Login
Login
 Cart
Cart