What would it be like if, instead of ordering your favorite coffee mixture every month, it were delivered to your doorstep just when you need it? This is the strength of the subscription economy.
Business models, such as streaming services and curated beauty boxes, have enabled convenient, consistent client patronage and recurring income. This is not a trend, but rather a business strategy that is a transformation for eCommerce brands.
The magazine and mail-order enterprise that started as a niche has grown into a global powerhouse in many sectors with digital advancement, the personalized needs of the consumer, and the allure of a steady flow of revenue.
In the modern world, brands use subscription models more and more actively so that they can retain their customers while establishing deeper relationships with them. When done right with the combination of value, flexibility, and personalization, the subscriptions stop being a set of sales strategies and turn into services.
A One-Time Buyer into a Lifetime Customer
Conventional eCommerce is usually pegged on a one-time purchase. However, the latter model is on the back foot, as the costs of acquisition are on the rise, and brand loyalty is decreasing. With a subscription-based model, the narrative is different. Every purchase is a starting point for a long-term relationship.
Businesses shift their focus from monthly conversions to building customer loyalty, minimizing churn, and maximizing lifetime value. In return, subscribers enjoy convenient, cost-saving, and personalized experiences that deepen their connection with the brand.
The change has enabled businesses such as Dollar Shave Club, Stitch Fix, and Blue Apron to create not only steady incomes but also brand communities and future loyalty.
Why Subscription-Based Models Are Booming
The subscription-based business is taking over the current business scene, be it a streaming service or a product box. This shift goes beyond convenience—it’s transforming how businesses operate and how consumers prefer to engage with products and services.
1. Predictable Stable Revenue Streams
A stable revenue is a game-changer for the business. In comparison to the single sales that are subject to fluctuations and are thus a nightmare to forecast, subscriptions come with regular earnings monthly.
This standardizing model enables businesses to strategize with confidence, be it the recruitment of new employees, initiating advertising campaigns, or investing in product development.
Understanding of predicting the cash flow assists businesses in minimizing financial tension and developing more effectively. The move to this model by many businesses is not a surprising fact.
A good example is Netflix. Its financial basis altered entirely when it shifted gears towards disc-based video rentals to an inexpensive streaming-based subscription service.
It currently makes billions of dollars in monthly revenue compared with the sporadic rental payments it received in the past, with more than 260 million subscribers.
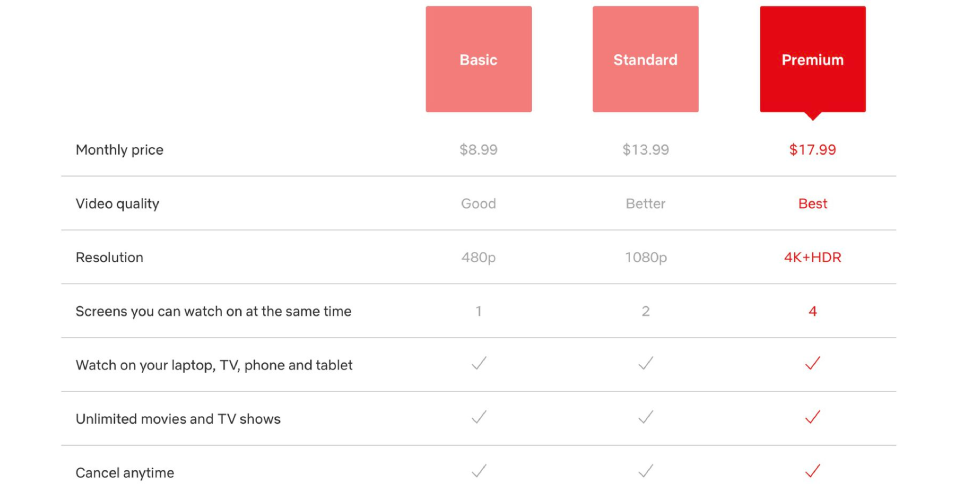
The sales energize fresh productions and refinements of the platform. In the same way, Adobe switched its software (such as Photoshop and Illustrator) to the Creative Cloud subscription.
This change stabilized sales and provided a continuous update to the users, which strengthened the continuity of customers and brought easier profits to the business.
2. Enhanced Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
Subscriptions do not simply mean the repeat purchase; they also convert one-off purchasers into long-term consumers. Rather than make a single sale in the amount of $50, a company can make hundreds-maybe thousands, in the long run when a subscriber is paying $10 a month.
This increased offering comes at a huge cost to lifetime customer value, one of the growth indicators in the business. Companies can spend their resources on current customers and not always seek new ones, as this will be cost-effective and satisfying.
A good example is Dollar Shave Club. Rather than seeing people coming in and buying razors once they found their way into the stores, they instead developed a monthly subscription whereby this simple grooming tool could be turned into an everlasting income.
Spotify retains the user based on curated playlists, exclusives in podcasts, and the ability to listen to music without an active internet connection. They develop the relationship, and the listeners become lifelong subscribers who keep on adding revenue, year after year.
3. Data Gathering & Individualization
Among the most significant benefits of the subscription model, one must note the constant flow of user information it introduces.
Each interaction (what people see, what they click, what they skip, what they rearrange) means that the companies can get some insights to get closer to knowing what people like individually.
This approach enables smarter suggestions, prompt offers, and customized content, which make customer loyalty stickier and less prone to cancellations. The more a person remains subscribed, the more helpful and factual that customization will be.
Such is the case with Amazon. By subscribing to its Prime, it tracks its purchases, watching patterns, and even tastes in music. The latter is leveraged to provide suggestions and ensure that content of high relevance is served to the users, thereby keeping them within the ecosystem.
4. Changing Consumer Habits
Consumer behavior has shifted dramatically. Today’s shoppers crave convenience, flexibility, and a sense of control. Subscriptions cater to these needs perfectly—they save time, automate repeat purchases, and allow users to easily tweak or cancel their plans.
For people juggling work, family, and digital overload, removing the need to make frequent buying decisions is a major relief. It’s not just about getting products; it’s about simplifying life.
Peloton understands this deeply. Instead of forcing customers to shell out thousands upfront for a fitness bike, they offer a more approachable monthly membership. This fee includes access to live classes, performance tracking, and a motivational community—all of which create stickiness over time.
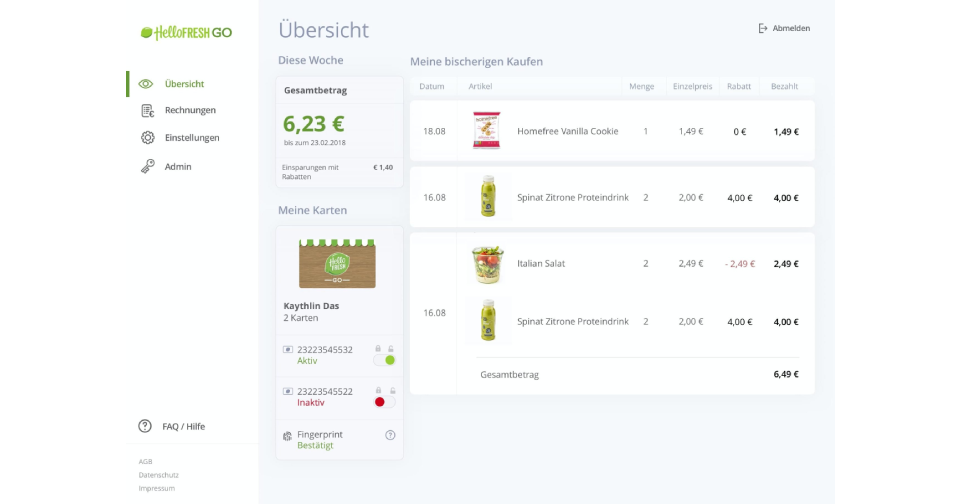
Similarly, HelloFresh delivers ready-to-cook meal kits weekly. Subscribers can choose their menus, pause deliveries, or skip weeks entirely. The convenience of getting meals planned and prepped at your doorstep, without the grocery store hassle, fits perfectly into the modern lifestyle.
5. Lower Customer Acquisition Costs Over Time
Acquiring new customers costs a lot of money- advertisement, promotions, and inducements all add up. Within subscription-based models, that script is reversed with the emphasis on retention. After a customer has enrolled, they should aim to ensure that they nurture that customer as opposed to giving them replacements often.
This saves marketing costs as time goes by and enhances profit margins. A loyal customer base is an asset that continues to pay off month after month without having to constantly re-engage the customers.
See Apple. By subscribing to services, such as iCloud, Apple Music, or Fitness+, a person is likely to derive some value and continue using them because of the easy interchange between gadgets of Apple gadgets.
Such an ecosystem lock-in diminishes the necessity of eye-catching advertisement campaigns; people become captivated with the experience.
Similarly, The New York Times has built a massive digital subscription base. By delivering quality journalism and personalized newsletters, they’ve significantly reduced their reliance on one-time newsstand buyers, saving on acquisition costs and boosting lifetime value.
6. Eco-Conscious & Minimalist Trends
The current and, especially, younger consumers find themselves sticking to the thought of how they can contribute to the environment through their purchases. Numerous people are attracted to the brand of subscription that suits their ideals, and those who believe in green and environmentally responsible consumption.
Instead of mass purchasing or over-consuming, they would like to have fewer and purposeful deliveries, which would reduce waste and promote reusing. Grove Collaborative has made the most of such an idea.
They sell green home and personal care products in reusable packaging, and they also provide their products on a regular schedule. This will not only save the use of plastic but will also foster a long-term relationship with the eco-friendly customers.
Rent the Runway is the other example. Their online fashion rental product subscription-based model allows users to access designer clothing without wasting and spending money on new pieces regularly.
It is trendy and environmentally conscious, which will allow the user to take care of their image and adhere to the principles of the circular economy.
Types of Subscription Models in eCommerce
Not all subscriptions are created equal. Different formats suit different industries and customer needs.
1. Replenishment Models
The replenishment subscription is made convenient. They can automate the shipment of their daily needs, which the consumers consume daily, such as toiletries, health supplements, household products, or pet care products.
Subscribers do not have to remember that they need to replenish their supply and can receive the needed product on a routine basis. This model avoids and deletes the tediousness of going into important things. It is particularly favored by consumers with hectic lifestyles who tend to value the set-it-and-forget-it types of products.
It guarantees long-term income to businesses as they gain the trust of their users with regular patterns. The likelihood that the products might be kept in the long run is high because they tend to be necessities.
The long-term result is a good basis for customer loyalty, and it can provide options for add-ons and upsells without having to employ heavy selling techniques.
It is based on convenience and reliability, and both parties benefit from it, as the customer knows when it will arrive and the business has a steady stream of customers.
2. Curation-Based Subscriptions
Curatorial models concentrate on the pleasure of discovery. Unlike monthly subscriptions of the same thing, these subscriptions delight and surprise customers with carefully chosen items tailored to their tastes, interests, and lifestyles.
These models tend to focus on personalization, so they are based on user preferences and will customize each delivery to be more individual. They are doing fine in niches where diversity and discovery matter, including fashion, wellness, books, or gourmet food.
Curation creates an emotional bond; people do not purchase merchandise or an outfit, they purchase into a narrative or a way of life. Such a model is successful when you are ready to anticipate, and it is able to build a great emotional connection between the customer and the brand.
In the long run, such surprise-based encounters typically create a sense of community, bottom-up content creation, and interaction that draws individuals to continue a subscription.
Birchbox is a popular beauty subscription-based model that sends customers a monthly box filled with personalized skincare, haircare, and makeup samples, helping users discover new products tailored to their profiles.

3. Access-Based Models
Subscriptions based on access are designed to provide customers with valuable perks beyond physical goods. These models offer benefits such as priority access, member-only discounts, early releases, or premium materials, giving customers exclusive features they highly value.
What subscribers really pay for is the feeling of belonging to something privileged or elite. These models are especially effective for companies with a broad ecosystem of products. Companies add value to the service by bringing together different perks in a single subscription package.
The strategy promotes customer loyalty since the consumers become used to the advantages and are less inclined to relinquish them. It also establishes an in-built motivation to come back again.
When executed properly, access-based models build long-term relationships and create a sense of exclusivity that ordinary offerings cannot match. The more valuable the benefits a brand provides, the more crucial the subscription becomes for its users.
4. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
The SaaS model has transformed technology usage for individuals and businesses by replacing traditional software purchases with subscription-based access to cloud platforms. Customers benefit from automatic updates, easy access across various devices, and affordable pricing.
For businesses, this shift turns large upfront expenses into smaller, predictable monthly payments, improving cash flow and reducing financial risk. Overall, SaaS makes software more accessible, flexible, and cost-effective, enhancing user experience while simplifying maintenance and upgrades.
For providers, SaaS guarantees steady recurring revenue. It’s attractive to users because they always have the latest features without needing manual upgrades or reinstallations, ensuring their software remains up-to-date effortlessly, improving convenience and eliminating downtime or compatibility issues.
It can also help companies collect real-time data about users in order to maximize performance and user experience. With digital work and remote cooperation increasing, SaaS has earned the status of a keystone of most businesses.
Whether creative tools or business platforms, the SaaS model ensures customers stay continuously connected to a service that evolves with their needs, providing ongoing improvements and adaptability to deliver a consistently relevant and up-to-date user experience.
5. Hybrid Subscription Models
Hybrid models are a mix of features of the other forms of subscriptions and provide a more fluid and extensive experience. These could combine curated product delivery and replenishment, and combine access-based benefits with a software platform.
The trick is flexibility. Hybrid subscriptions provide consumers with the option of customizing customer engagement. This business model is able to support varied needs in just one package, and, at times, it makes the subscription seem even more worthwhile and less costly to stick with.
It is an excellent solution to attract the attention of more people without creating completely new services. Companies that have applied this model can be experimental with different features and levels and can alter them according to customer response and action.
To consumers, hybrid models result in convenience, choice, and a feeling of control. Discovery, utility, and exclusive benefits combine to deliver a balanced experience that does not feel transactional, but rather, relationship-oriented.
Amazon Prime exemplifies a hybrid subscription model by combining product replenishment, curated recommendations, exclusive access perks, and digital services like Prime Video and Music.
This multifaceted approach offers users convenience, personalization, and value, fostering long-term loyalty across shopping and entertainment experiences.
Challenges in Subscription Commerce
- Subscription Fatigue
Consumers may feel overwhelmed by too many subscriptions or feel trapped. Offering flexible plans, easy cancellations, and clear value helps reduce fatigue. - Churn Management
Even satisfied users can cancel. It’s crucial to identify churn triggers and implement re-engagement strategies like personalized offers or reminder emails. - Payment and Billing Friction
Failed or expired payments can lead to involuntary cancellations. Using automated retry systems, reminders, and multiple payment methods can reduce this risk. - Competitive Saturation
With countless businesses offering subscriptions, differentiation is key. Focus on user experience, consistent value, and innovation to stay ahead. - Regulation and Compliance
Laws like GDPR and CCPA require transparency in how customer data is used. Clear cancellation policies and ethical practices foster customer trust. - Supply Chain Dependencies
For physical products, delays, stockouts, or inconsistent deliveries can frustrate customers. Efficient, responsive logistics are essential to maintain loyalty.
Conclusion
Subscription-based models have become a powerful strategy for building lasting customer relationships and generating predictable revenue. By offering convenience, personalization, and flexibility, they transform one-time buyers into loyal, long-term users.
Whether through replenishment, curation, access, or hybrid formats, these models meet evolving consumer demands while enhancing customer lifetime value. However, success requires more than automation—it demands constant innovation, seamless user experience, and ethical transparency.
Brands must also address challenges like churn and subscription fatigue to stay competitive. In today’s fast-paced digital economy, well-executed subscription models offer not just recurring income but deeper engagement and sustained relevance.
Acowebs are the developers of the WooCommerce Product Labels which let customers include custom product labels or product badges for the WooCommerce products. WooCommerce sales badges plugin provides you with different label styles and customizations for labels. It offers a easy-to-use UI to add labels to the selected products or categories and woocommerce email customizer using which you can easily build and customize WooCommerce emails with a drag-and-drop user interface.









 Login
Login
 Cart
Cart