Table of Contents
Payment processors and payment gateways serve integral functions in modern digital commerce. They assume distinct yet complementary roles in supporting electronic transactions.
A payment processor oversees the secure transfer of funds between buyers and sellers during a transaction. Meanwhile, a payment gateway provides a protected channel for transmitting transaction details between all involved parties.
As businesses and customers continue migrating away from cash toward digital payments at an accelerated pace, comprehending how these entities work has become important for operating effectively in today’s digital marketplace landscape.
This article aims to explore payment processors and payment gateways in depth. It will outline their specific functions, highlight key distinctions between the two, and outline the benefits they offer businesses.
By elucidating their precise operations and implications for online transactions, readers can gain meaningful insight for selecting appropriate solutions tailored to their needs.
Defining Payment Processors
Payment processors are essential third-party companies that power digital commerce.
They authorize payments and seamlessly transfer money between parties, enabling convenient checkout experiences for consumers across online shopping channels whenever electronic forms of payment are used.
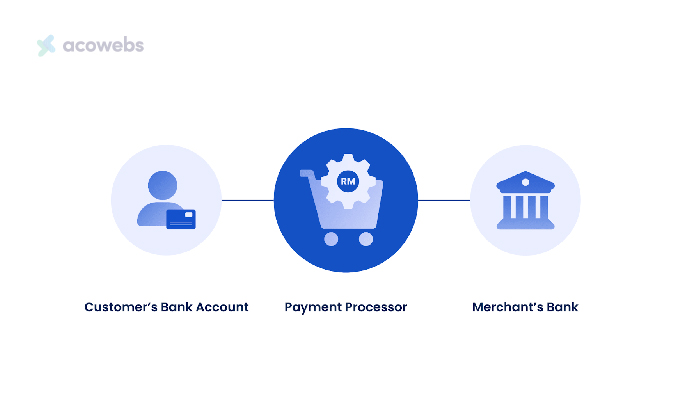
Specifically, payment processors operate behind the scenes to process transactions made with credit cards, debit cards, and other options, including digital wallets. They ensure secure fund transfers between businesses, customers, and banking organizations.
Payment protectors also undertake responsibilities like validating payment details, acquiring authorizations, and dealing with compliance requirements. This allows merchants to accept different online payment solutions through a single connection to the payment handling system.
Businesses gain advantages from the services of payment processors as it enables them to receive electronic payments without needing direct interfacing with each individual bank and credit card company.
Key Functions of Payment Processors
- Intermediary Role: Payment processors connect merchants to the various financial institutions involved in transactions, including the merchant’s acquiring bank and the customer’s issuing bank. They facilitate communication and coordination between these different entities.
- Transaction Authorization and Processing: Processors verify transaction details and secure approval from the customer’s bank or credit card company to confirm sufficient funds. Next, they process the payment by routing the financial data and initiating the transfer of money between parties.
- Security and Compliance: Payment processors implement security measures like encryption to protect sensitive payment information from theft or fraud.
They also manage risks like chargebacks and ensure compliance with pertinent industry and government standards to keep electronic exchanges secure for merchants and consumers.
- Additional Services: Many processors offer ancillary services to add value for merchants. This can include reporting, reconciliation, data analytics, and even specialized support for particular industries or business needs to allow for streamlined digital transactions and commerce.
Examples and Services
- Popular Payment Processors: Prominent processors in the industry include Stripe, PayPal, and Square. They provide various services, from fundamental transaction processing to more sophisticated offerings such as banking-as-a-service solutions.
- Additional Services: In addition to basic handling of payments, these processors frequently supply merchant services, including payment gateways, point-of-sale systems, and tools for automated revenue and financial management. Tailored assistance like consulting and technical integration support may also be offered.
Payment facilitators play a core role in supporting today’s eCommerce and retail infrastructure by enabling a smooth transaction process. This proves integral to the growth and sustainability of businesses conducting digital and physical sales operations.
Defining Payment Gateways
A payment gateway is a crucial technology in electronic transactions that provides a secure connection for transferring payment details between a business, its customers, and the associated processing network. It acts as the digital intermediary that facilitates transactions, whether online or in-person.
Specifically, payment gateways encrypt and route sensitive financial data to the appropriate third-party processor for verification and authorization.
Gateway technology ensures transactions are securely authenticated by checking payment methods for validity and screening for potential fraud or suspicious activity.
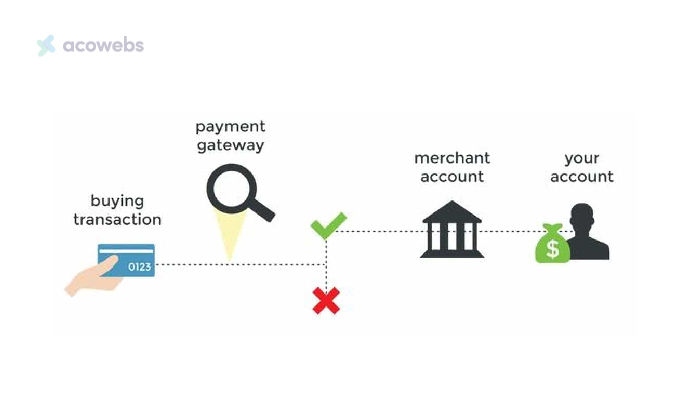
The gateway allows merchants to accept card payments without directly handling delicate customer information themselves. It serves as the checkpoint that safely transmits payment data to the back-end processors for review and fund transfer completion.
Key Functions and Architecture
The primary functions of a payment gateway include the encryption of sensitive payment data, the connection with a payment processor to facilitate transaction authorization, and the provision of fraud detection and prevention measures.
Depending on the setup, payment gateways can vary significantly in their architecture. Online transactions typically require application programming interfaces (APIs) for integration, while in-store transactions utilize physical POS terminals to connect to the payment network.
Products, Services, and Industry Applications
Payment gateways offer a range of services that extend beyond mere transaction processing. These services include online payment solutions, POS systems, card issuing, and acquiring.
They also provide platforms for global payment methods, partnerships, and detailed reporting on transactions, which are crucial for risk and fraud management.
Industries that commonly utilize payment gateways include eCommerce, retail, travel, and small businesses, reflecting the versatility and essential nature of payment gateways in various commercial settings.
Key Differences Between Payment Processors and Gateways
1. Role in the Transaction Process
Payment processors and gateways play distinct parts in processing transactions. A payment processor’s main function is to directly manage the processing and approval of payments. This involves securely finishing transactions smoothly and safely.
On the other hand, a payment gateway serves as an intermediary that securely transfers payment details. It enables contact between all parties engaged, such as the merchant, issuer, and collector.
In summary, a processor deals with the core processing aspect, while a gateway centers on transmitting sensitive financial data in a protected manner.
2. Scope of Services and Integration
Payment processors and gateways vary in the scope of services provided. Processors handle a wide range of functions, such as fraud prevention, chargeback management, and financial transfers between banks.
Gateways concentrate on securely transferring payment data. They frequently integrate more easily with business systems through elements like APIs, plugins, and pre-built modules. This streamlines the setup for merchants in comparison to processors.
In summary, processors offer a full suite of payment services, while gateways specialize primarily in transmitting payment details through strengthened system integration.
3. Necessary Components in Online Payments
Payment processors and gateways both play important roles in enabling online transactions. They cooperate to facilitate the acceptance of credit card payments over the Internet.
The technology system involves a payment gateway connecting the website’s shopping cart to the card processing network. A payment processor then guides the transaction through the processing network.
This joint effort ensures online purchases are carried out smoothly and securely. It provides value to both merchants and customers by approving digital exchanges of goods and funds.
In summary, processors and gateways work in tandem utilizing linked technical infrastructures to fulfill the task of internet-based payment processing.
How Payment Processors Work
Payment processors are integral in facilitating the execution of electronic transactions from the time when a customer makes a payment to the intricate procedures of an end-turn over to the merchant’s account.
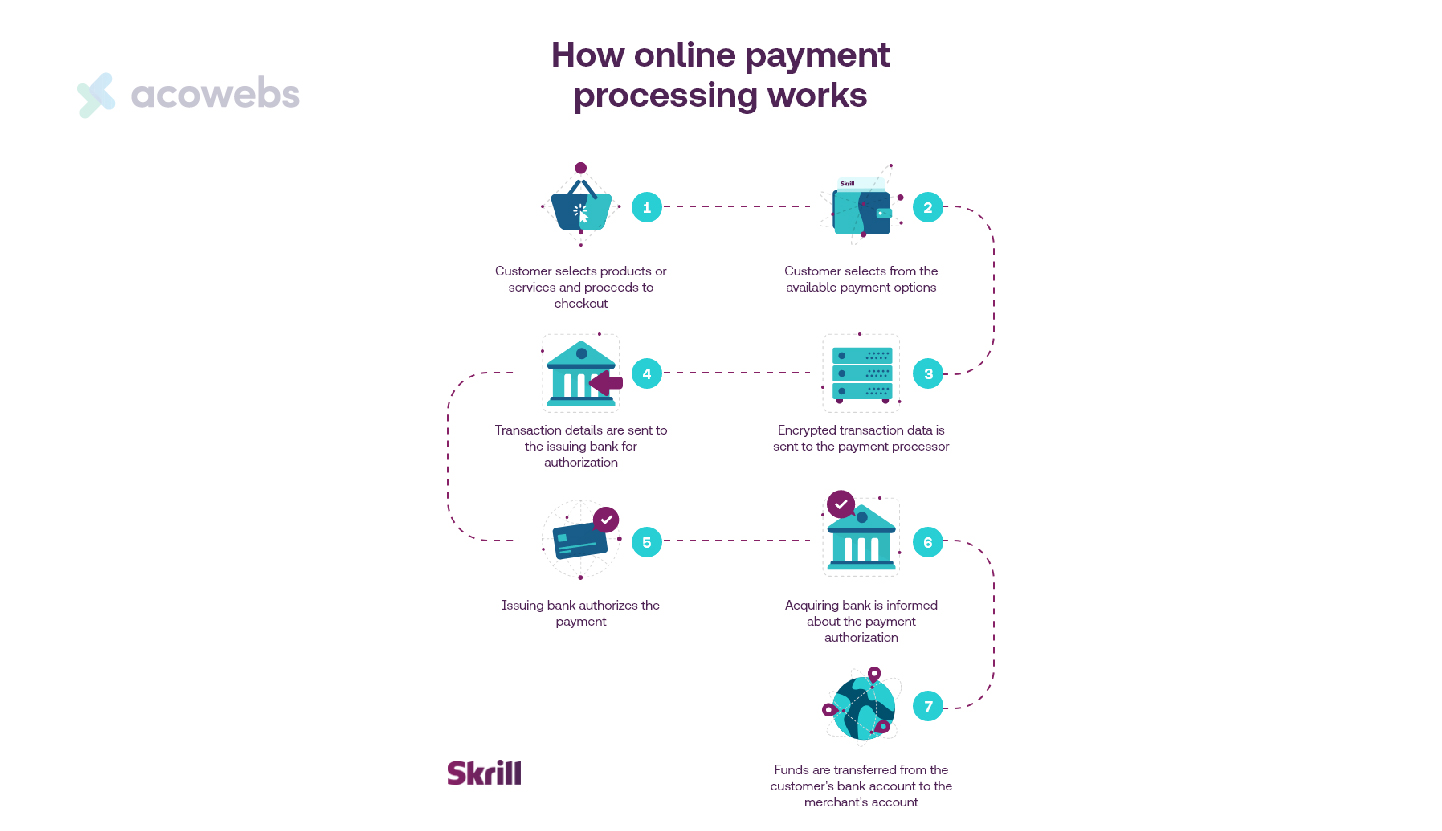
The infographic above from Skrill illustrates how payment processors work:
Step-by-Step Transaction Process
- Transaction Initiation: When a customer makes a purchase, their financial data and purchase details are securely submitted to the relevant entities like the payment processor, issuing bank, and acquiring bank through the card network.
- Request for Authorization: The payment processor then contacts the customer’s issuing bank to verify sufficient funds for the purchase.
- Security Measures: Sensitive financial information and details are protected during transmission between parties using encryption and tokenization technologies as arranged by the payment processor.
- Funds Transfer Coordination: Upon authorization, the payment processor facilitates the transfer of funds from the customer’s issuing bank to the merchant’s acquiring bank to complete the financial element.
- Credit to Merchant Account: The merchant’s bank account is credited with the transaction amount minus any applicable fees, concluding the financial aspect of the transaction for the business.
Detailed Processing Flow
The typical processing flow utilized by payment processors encompasses several critical steps:
- Payment Gateway Exchange: Firstly, the payment processor obtains encrypted financial information from the payment gateway.
- Issuing Bank Confirmation: The processor then sends this information to the customer’s financial institution to seek approval and awaits a response.
- Authorization Communication: Upon receiving the authorization from the issuing bank, the processor relays this approval status back to the payment gateway.
- Funds Settlement and Reconciliation: Lastly, the payment processor oversees the settlement of funds and provides assistance in reconciling and reporting details of the transaction.
Collaboration with Payment Gateways
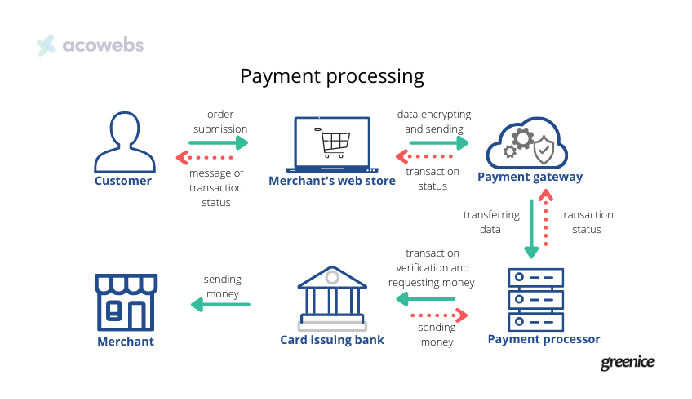
Payment processors and payment gateways work closely to ensure the seamless execution of transactions, as illustrated in the above image:
- Secure Data Transmission: The payment gateway encrypts and transfers the financial information to the payment processor, which is vital for maintaining security.
- Authorization and Fund Transfer: The payment processor then undertakes the important roles of obtaining authorization confirmation, synchronizing fund transfers between banks, and liaising with the customer’s financial institution.
- Final Transaction Communication: Upon processing completion, the payment processor relays the result back to the gateway, allowing it to update the business on the transaction status and conclude the process.
This integrated approach ensures that electronic payments are processed efficiently and securely, benefiting both businesses and consumers by providing a reliable and smooth transaction experience.
How Payment Gateways Work
Payment gateways occupy an essential position in carrying out smooth web transactions, serving as a channel for protected data transmission between customers and merchants. Here is a step-by-step description of their general working process:
Step-by-Step Operational Framework
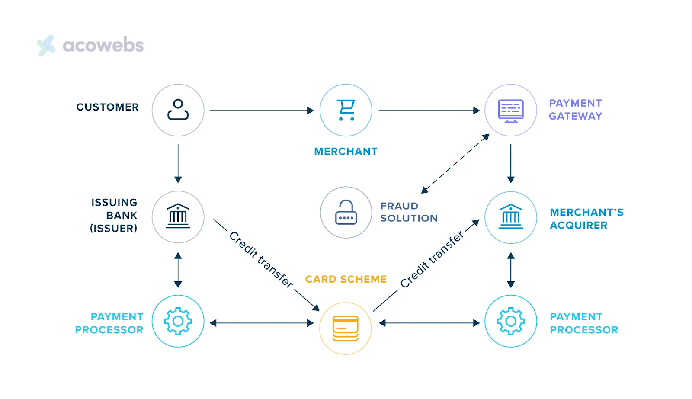
- Transaction Initiation: A customer initiates a purchase by entering their payment details on a merchant’s website. The payment gateway then encrypts this sensitive information.
- Fraud Checks and Data Transmission: The encrypted data undergoes fraud checks before being transmitted to the merchant’s acquirer.
- Authorization Process: The acquirer forwards this information to the card scheme and issuing bank to obtain transaction authorization.
- Communication and Completion: Once authorized, the payment gateway communicates this back to the merchant and customer, completing the transaction process.
Additional Services and Integration
Payment gateways are not limited to basic transaction processing. They offer a range of additional services and integrations:
- Acquiring Services: Some gateways provide acquiring services, handling the processing of card payments directly for merchants.
- Support for Various Payment Methods: In order to accommodate global customers, these gateways support multiple payment methods beyond traditional credit and debit cards.
- Integration Capabilities: Payment gateways often feature robust integration with other platforms, enhancing their utility and flexibility for businesses.
Industry Applications and Technical Support
The versatility of payment gateways extends across various industries, aided by comprehensive technical support:
- Wide Industry Application: From eCommerce to retail, payment gateways can customize their solutions to cater to distinct industry needs in various sectors.
- Developer Resources: They supply developers with comprehensive documentation like API references and software development kits to simplify the integration process.
By facilitating secure payments and offering robust assistance and technical integration options, payment gateways help improve the functional effectiveness of companies engaged in Internet commerce.
Benefits of Using Payment Processors
Payment processors present an opportunity to achieve numerous benefits that greatly increase the efficiency of business transactions and their level of security.
The below mentioned advantages are essential if a business wants to maximize the use of its financial transactions and, hence, enhance customer satisfaction potential.
Efficiency and Speed
- Transaction Time Reduction: Payment processors expedite the transaction process, cutting the time required to finalize payments from days down to just seconds, boosting overall efficiency.
- System Integration: Integration with current business systems simplifies data administration, permitting smoother importation and storage of electronic information across platforms.
Cost Management and Security
- Reduced Transaction Costs: By removing the requirement for paper checks and related processing charges, businesses can save on printing, postage, and secure document disposal expenses.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Sophisticated protection methods like tokenization and encryption are utilized to safeguard sensitive information, considerably lowering the risk of data security incidents.
- Fraud Prevention: Payment processors employ secure and encrypted channels for dealings, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access sensitive information.
Customer Experience and Business Growth
- Diverse Payment Options: Providing a range of payment options, like credit cards, debit cards, and mobile digital wallets, caters to client preferences and enhances satisfaction levels.
- Business Scalability: Payment processors provide the flexibility required for businesses to adapt and expand in the quickly transforming payments environment.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Direct relationships with payment processors ensure expert assistance, superior customer service, and potential cost savings, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Benefits of Using Payment Gateways
Payment gateways provide a variety of benefits that simplify and safeguard the payment process, boosting the experience of both merchants and consumers. Here are some major perks:
Comprehensive Systems and Advanced Security
Payment gateways provide comprehensive payment systems that enable a broad scope of functions like instant payments and order status updates essential for keeping transaction records up to date.
They adhere to strict security requirements such as PCI DSS, ensuring the protection of sensitive payment information through advanced security protections like encryption and tokenization.
This robust security framework notably decreases the dangers of data security incidents and fraud, safeguarding both commercial and consumer interests.
Enhanced Customer Experience and Global Reach
The adaptability of payment gateways to accept various payment types and currencies caters to a global client base, facilitating international payments and supporting worldwide growth strategies.
They enhance the customer experience by offering customizable checkout selections and automatic recurring checkout, which streamline the purchasing process and boost customer satisfaction.
The option to customize and incorporate these systems with existing business platforms permits a frictionless user experience, cultivating customer loyalty and potentially raising sales.
Operational Efficiency and Business Growth
Payment gateways simplify the financial administration for businesses by automating payment collection and reducing the time involved in managing transactions.
This automation extends to revenue and finance, with features like subscription management and sales tax automation, which help businesses scale and adapt to changing market conditions.
The reduction in declined transactions and the quick processing of payments ensure that businesses maintain a steady cash flow, which is crucial for sustained growth.
Choosing the Right Payment Processing Solution
When selecting a payment processor, businesses should carefully evaluate several important factors to ensure they choose the best partner to handle transactions safely and efficiently.
Key Considerations for Payment Processors and Gateways
- Fees and Pricing Structures: Fees are a major concern, so processors offering transparent, competitive pricing deserve examination. Flexible structures like flat rate, interchange plus, and tiered options allow customization to a company’s volume and average sale amount.
- Security and Compliance: Security cannot be overstated. Protecting sensitive financial data from theft or fraud is mandatory, given the latest data breach reports.
The Privacy Rights Clearinghouse (PRC), a nonprofit organization based in the United States, reported there were 35,167 instances of data breaches across multiple sectors from January 2002 to October 2023.
The total number of records compromised in these breaches surpassed 17 billion.
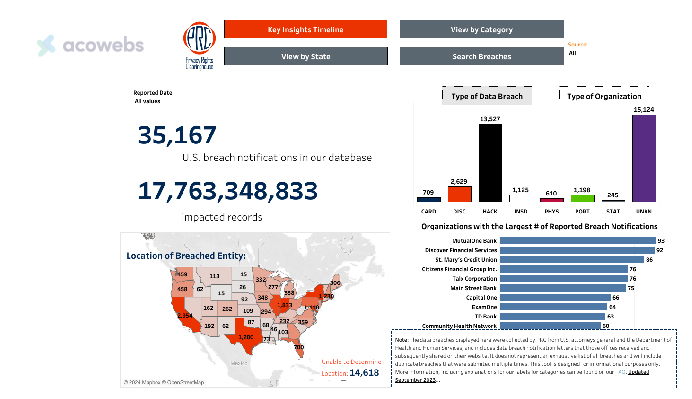
Seeking processors with robust security like PCI compliance, encryption techniques, and fraud monitoring capabilities minimizes these risks.
- Payment Methods and International Support: For enterprises targeting wider markets, the ability to process an array of prevalent payment methods takes priority. Major credit and debit cards, emerging digital wallets, and international currency exchanges facilitate growth. The right processor enables acceptance of preferred tender types worldwide.
Integration and Customer Support
- Ease of Integration: When choosing a payment processing solution, a major consideration is how easily it can integrate with a business’s current technology setup. Looking for a provider that allows seamless connection to enterprise resource planning (ERP) programs and accounting applications streamlines workflows.
- Customer Support and Services: Reliable customer support is critical, especially when dealing with payment disruptions. Opt for providers that offer comprehensive support and services, including transaction processing, settlement of funds, and dispute management.
Strategic Business Considerations
- Scalability and Flexibility: When choosing a payment processor, scalability and flexibility are key factors to consider given evolving business needs. The solution should accommodate increased transaction volumes easily and support multi-currency capabilities.
- Contract Terms and Cancellation Policies: Equally important are contract terms and cancellation policies. Merchants must comprehend the stipulations and timelines specified within agreements to circumvent problems, unforeseen costs, or obstacles exiting these arrangements if required.
By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can choose a payment processing solution that not only meets their current needs but also supports their growth and adapts to future challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, through this in-depth exploration, we’ve learned that payment processors and gateways each play important roles in the digital transaction ecosystem.
Processors facilitate the efficient and secure transfer of funds between parties, while gateways serve as secure conduits for transaction data exchange. Comparing their functions has offered key insights for optimizing operations and enhancing security to elevate the customer experience.
When selecting a payment solution, businesses should choose one that meets current needs cost-effectively while possessing flexibility for future growth.
Making informed choices in this area allows firms to streamline operations, safeguard transactions, and provide customers with a simple, satisfying payment process. This fosters business expansion and maintains a competitive advantage in digital commerce.
Acowebs are the developers of the WooCommerce Product Labels which let customers include custom product labels or product badges for the WooCommerce products. WooCommerce sales badges plugin provides you with different label styles and customizations for labels. It offers a easy-to-use UI to add labels to the selected products or categories.








 Login
Login
 Cart
Cart