Product pricing can be challenging because, on the one hand, overpricing can cause customers to abandon your store for the competition, while underpricing can cost you your profits.
There is also the perception that cheap products are low quality, which could further affect your sales.
Proper product pricing is, therefore, a combination of art and science, requiring you to consider several factors, such as competitors’ pricing and the link between price and quality.
Correct pricing will surely impact your sales and revenues positively, while incorrect pricing will have a reverse effect on your sales and profits.
Given the many factors you have to consider when setting the right price for your products, this article will demonstrate what you should do in an easy-to-use guide.
Factors that go into creating a pricing strategy
Before we discuss the practice of product pricing, let’s have a glimpse of a few things that you should consider when setting the price.
Your business goals
How high or low you price your products will depend on your business objectives. For instance, if your objective is to grow by reaching more high-net-worth customers, you are welcome to use premium pricing on high-quality products.
However, if your goal is to increase sales volumes in your existing market with many competitors, then moderate to low-cost products will sell more.
Ensure to incorporate your business goals in your pricing strategy for more informed decision-making that aligns with your target market.
The value of your product
Your product’s value can be determined by factors such as profitability, marketing position, utility, and customer perception.
There are also other ways to value a product, such as collaborative estimation, whereby the price is tied to the qualitative value the product or feature delivers to the business or user.
Despite the approach used, there is no one approach that applies to all businesses, and considering how other players in the market are pricing a product will give you a better idea if you are over-or under-pricing.
ALSO READ: How to effectively use Heatmaps for your eCommerce store
Customer needs

Customers‘ needs affect product pricing in three ways:
First, buyers must determine if the product offers value, after which they will consider the price to attach to it. Second, the number of buyers – many buyers cause the demand to increase, leading to high product pricing, and vice versa.
Third, the sensitivity of customers to price changes should determine how high or low to price your products.
Durable goods (e.g. electronics) are more price elastic than basic goods or necessities like health products and food, and luxuries (e.g. jewels).
You should study your market to determine what motivates customers to buy to avoid scenarios whereby your pricing does not tally with the customers’ needs.
With this information in mind, it’s time to go deeper into pricing strategies.
How to price your products?
There is no one particular approach for pricing your products, but the following steps will give you an idea of the factors to consider when creating a pricing strategy for your eCommerce business.
Familiarize yourself with the target market
Your target customers may have specific needs, but in addition to that, you must understand their economic background to ensure your product prices are within their budget.
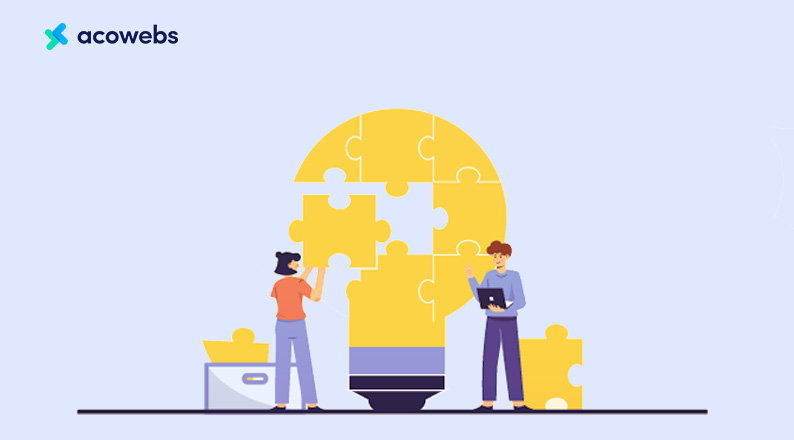
Start by profiling potential buyers by creating a buyer persona. Tools like Hubspot’s Make My Persona will give you an idea of who your target customers are, their income bracket, and their needs and expectations.
Below is an example of a buyer person created using the Hubspot tool – it tells you the age group of the target customers, the highest level of education, job title and responsibilities, the industry of operation, social networking platforms, and preferred mode of communication, among others.
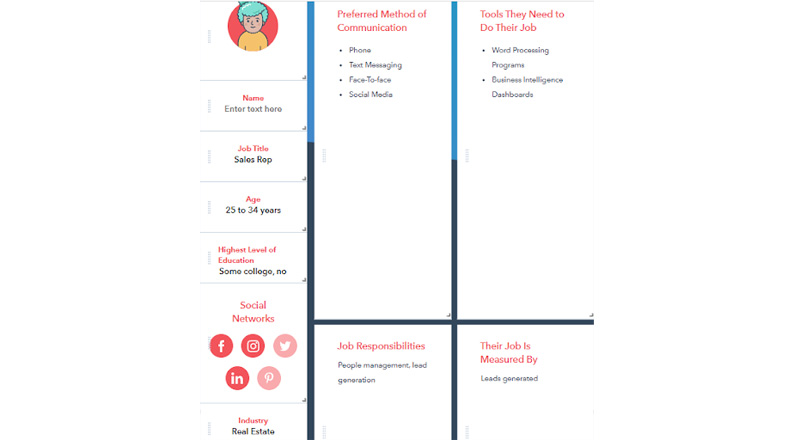
How do you get to identify your customers’ buyer persona?
- Conduct research using tools like Facebook ads, Google Analytics, Google Keywords, SurveyMonkey, and Questback to gather information on the location of your buyers, their likes, purchase frequency, and demographics.
- Conduct surveys on your existing customers to understand their demographics, what they like, their interests, expectations, and tastes and preferences.
- Send informal surveys through email campaigns containing hypothetical product descriptions and ask the audience to quote the price ranges they would attach to the items.
- Follow industry news and trends to understand consumer habits/buying patterns, preferences, and industry innovations.
- Hire a third-party research agency to gather market research data about your target market.
Once you determine who your ideal customers are, their spending habits, budget consciousness, motivation, status, and psychological susceptibility, you can create a pricing plan that suits their budget, while remaining within the competitors’ pricing range.
ALSO READ: How to Customize WooCommerce Invoices & Send After Each Order
Set a base price based on your industry’s pricing strategies

The next step in setting product pricing is to conduct research about the common pricing strategies in your market because a pricing model that works in one industry may not always work in another.
By reviewing the pricing strategies that work best in your industry, you eliminate guesswork, giving you a certain level of confidence.
You can conduct competitor and market research using survey tools like SurveyMonkey or market research apps, enabling you to gather reliable and detailed data on the prevailing market prices.
There are 4 main pricing strategies you can adopt for your eCommerce store:
Cost-plus pricing
Cost-plus pricing is a simple, common pricing strategy that is obtained by adding the total production costs to the percentage markup to determine the final selling price.
Under this approach, you sum up the direct labor, direct material, and overhead costs for your product and add a markup percentage to the figure to obtain the product price.
Therefore, if the total labor, material, and overhead costs of a given product are $40 and the standard markup percentage (desired profit margin) for the retail industry is 50%, the final price of your product will be $60 (40*1.5).
Cost-plus pricing:
Price = Cost * Desired Profit Margin
or
Price = Cost + Desired Profit
This simple product pricing approach puts you in line with the competitors’ pricing while enabling you to reap profits from every product you sell.
Market-oriented pricing
Market-oriented pricing (competition-based pricing) entails comparing the prices of similar products within a given market.
For instance, if your competitors are selling a product at $150, market-oriented pricing dictates that you sell at the same price.
Alternatively, you can take the prices of the top 3 competitors and average them to come up with the right price for your products and services.
You can also choose to price your products above or below the market price instead of copying what the competition is selling at.
When you price above the market, you are intentionally branding yourself as a high-value brand with better-performing or higher-quality products than the competition.
On the other hand, if you price below the market, you are creating the impression that you offer the best prices, thus, luring more customers to your store.
Still, you must consider your production costs plus product quality compared to competitors before settling on one market-oriented pricing tactic.
ALSO READ: 10 Ways to Create Product Videos for eCommerce
Dynamic pricing
Dynamic (demand) pricing is time-based, meaning that businesses set adjustable/variable prices for their products and services, depending on the prevailing demand in the market.
When you follow this practice, you must monitor and change your product prices several times in a day, week, or month to better suit the purchasing habits of your customers.
Brands like Amazon and Uber use dynamic pricing to take advantage of surges in demand, hence, increased profits.
During seasons like Black Friday and Christmas, Amazon adjusts its prices to reflect market conditions (supply vs demand) and competitors’ pricing.
At the bottom-right corner of the image below obtained from Amazon, you can see the prices offered by other sellers for a NutriBullet NBR-1201 12-Piece High-Speed Blender.
NutriBullet sells the product for $80.90, which is lower than other sellers like Olive Branch Enterprises, where the item goes for $81.00. Stelli Products have set their price quite high, at $88.99, all exclusive of shipping costs.
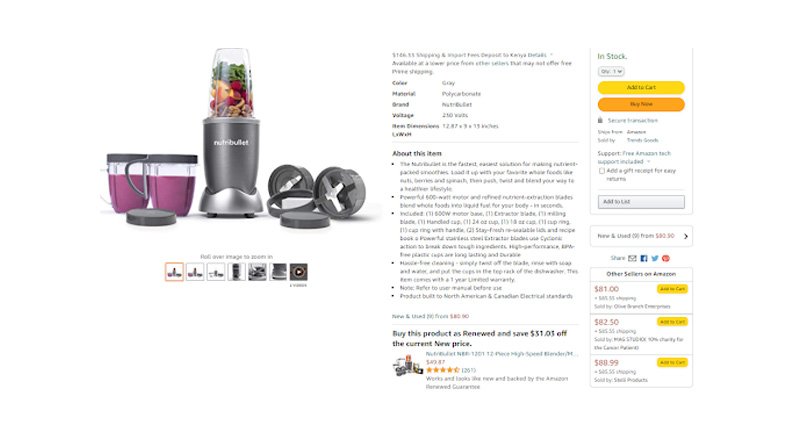
How you set or adjust your product prices will definitely affect your sales and profits. Thus, you must consider factors like production costs, target market, and product quality, even as you adopt the dynamic pricing model.
Value-added pricing
The value-based product pricing approach entails pricing products according to the value customers place on them.
Factors, such as availability, quality, innovativeness, performance, and exclusivity affect customers’ perception about the value of the product or service.
You must conduct research to understand how your competitors are pricing similar products, giving you an idea of what customers are willing to pay for them.
This is a great way of understanding what your target customers think is important and ensure your products meet these expectations.
Therefore, even when the cost-plus pricing model dictates that you should add a 50% profit margin on your product, yet you know your target market can afford to pay a 70% profit margin due to the product’s value-add, you can adjust the pricing using the value-based approach.
This practice is best applied in a market where customers are not budget-conscious.
You can always enhance your product benefits in order to justify the higher pricing by facilitating convenience, branding your products, setting a trend through innovativeness, and providing exceptional customer service.
Other common pricing strategies:
- Hourly pricing – Suitable for businesses offering services. Here, you will invoice customers based on costs incurred and hours your team spends on a given project or deliverable.
- Performance-based pricing – This approach entails pricing your products depending on their performance.
- Discount pricing – You can start pricing your products high after which you offer discounts or reduced prices. You can also start with discount pricing on all new products for a limited duration in order to attract customers and enhance sales.
- Loss-leader pricing – This product pricing approach entails selling products at a price lower than the production cost with the goal of attracting customers who will, in addition, buy other items with a higher profit margin.
- Anchor pricing – Here, you display your product’s regular (imaginary) price, after which you visibly lower it on your product pages, creating the impression that shoppers are getting an incredible deal. You can also implement this tactic by displaying two products alongside each other, with one model being visibly cheaper than the second alternative.
Companies that sell software or IT-related services, like Zoom, apply the anchor pricing model frequently.
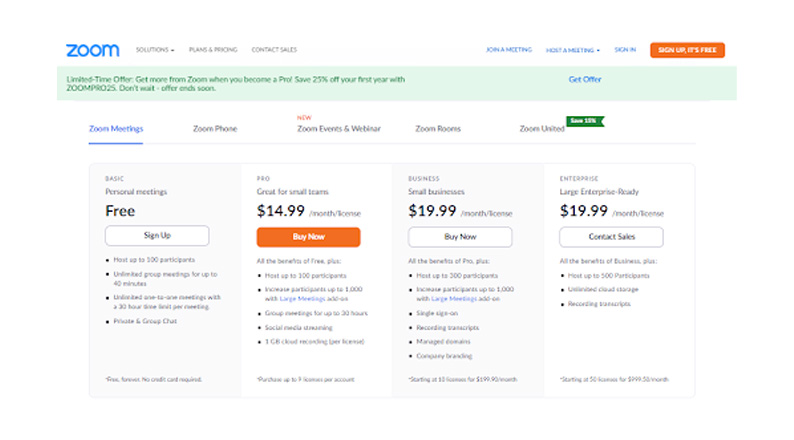
Determine your production costs
While there are many factors that go into how you price your products, cost is a key element that you must consider.
The main costs that go into production include:
- Direct payments: this input refers to the money you have spent developing your product or service. You can consider factors like time spent and amounts paid to manufacturers or suppliers for a given product.
- Variable costs: These are costs that increase with the volume of output, such as materials, marketing, packaging, etc. They also include delivery/shipping costs, inventory, import duty tax, credit card fees, etc.
- Fixed costs: These are costs that remain constant, irrespective of the volume of sales, such as wages, utilities, rent, etc. These can also be one-off startup costs and monthly fixed expenses like business license, website themes, advertising costs, and salaries.
To determine your production costs, break down the creation into tasks, such as shipping, inventory, labor, etc. You can then monitor the costs that go into every product by dividing the costs by the volume of output. By optimizing these factors and refining your pricing strategy, you can increase agency profit by driving up your margins without sacrificing quality or customer demand.
You should also use a project management tool to monitor the number of hours spent completing a given task. Additionally, implementing project development methodologies such as agile scrum maximize real-time feedback and and adaptability to create a fully functioning system Quantify the time and add it to your production costs.
A tool like a breakeven calculator will come in handy because it helps you determine your total variable costs per unit of output, as well as the breakeven cost.
The calculator will tell you the number of items you need to sell to breakeven (cover all your expenses) and how many more to sell to reach your target price.
Once you have an idea of your production costs and breakeven point, you must consider how to achieve the desired output or profitability level.
You can either lower your production costs (such as through efficient processes or optimization using technology) or increase your revenues.
Higher revenues/profits are achievable by increasing the level of sales or raising the price of your products, or both.
If you choose to raise your product prices, consider the following factors:
- Will the approach lead to loss of customers to the competition?
- Can you adopt cost reduction strategies instead?
- Can you raise prices on more profitable/valuable products?
ALSO READ: 10 Foolproof Ways to Improve eCommerce Email Engagement
Determine your profit margin
By now you understand your customers’ needs, you have researched the market to determine the best pricing strategy, and you have an idea of your production costs.
Next, you have to settle on the profit margin to set for your products, while ensuring to cover your production costs.
At the same time, you have to keep the selling price at the prevailing market rate or even higher depending on the pricing strategy you are using.
Having gathered all the necessary information, you should set your profit margin using the following formula:
Profit Margin = [(Selling Price – Production Cost) / Selling Price] * 100
A Profit Margin Calculator is a useful tool for calculating the profit margin for your products:
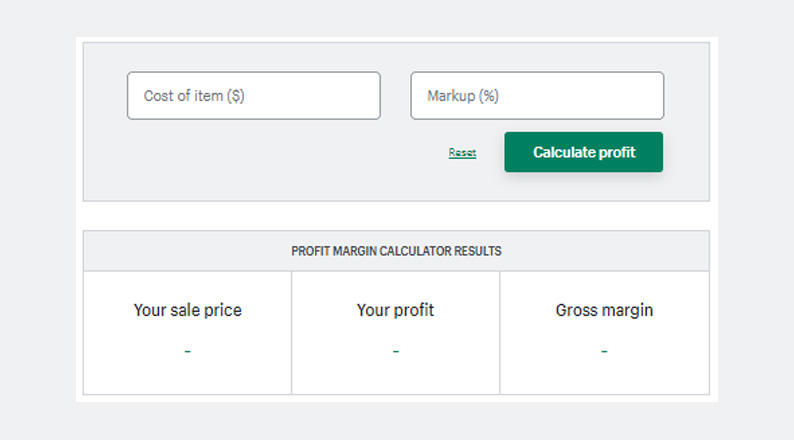
Remember to keep your product prices and profit margins at levels that align with your business goals for growth and sustainability.
Consider other factors
In addition to setting your product pricing, you must take into consideration other factors that are likely to impact your future pricing.
Your business is likely to expand, leading to higher fixed and variable costs, suppliers are likely to change their payment terms, while consumer behavior and needs could change in the face of competition and market trends.
How do you cope when faced with such changes?
Adopting strategies like economies of scale will put you in a better position to improve your production efficiencies, hence, reduced costs.
For instance, you can outsource functional services like IT, HR, and other non-core activities, enabling you to cut down on production costs as well as concentrate on revenue generation.
You can also cut costs by buying your products or raw materials in bulk and negotiating prices with suppliers.
Keeping up with market trends and industry patterns is equally useful in ensuring your product pricing is in line with what is happening.
Changes in regulatory requirements, sales taxes, regional differences in consumer trends or disposable income, seasonal changes in buyer behavior, and environmental and ethical considerations, are a few factors that could present opportunities to either lower or raise your product pricing.
Remember gathering customer feedback and keeping watch of how competitors are pricing their products is useful in determining how to price your products.
Review your pricing strategy frequently
Finally, ensure to measure and keep track of your key performance indicators (KPIs), especially metrics that determine your revenue and marketing success.
Monitor your price-performance by consistently evaluating and adjusting your price and production volumes in order to maximize profits.
You should also link your KPIs to tools that can assess the impact of changes in production costs, price, and profit margins.
ALSO READ: UX Design Strategies for eCommerce Websites
Conclusion
Product pricing is both an art and science that requires balancing between what customers expect or how they value your product, your business objectives or profitability goals, market trends, and competitor pricing.
Over- or under-pricing can have negative or positive impacts on your sales and profits; hence, understanding how to price your products is very important to your eCommerce business success.
First, you must familiarize yourself with the target market, after which you should set your base price depending on the industry’s pricing strategies.
At the same time, you should determine your production costs and profit margin to give you an idea of the breakeven price and sustainable pricing.
You should also consider other factors likely to affect the price of your products and services and review your pricing strategy accordingly.
Acowebs are developers of Woocommerce bulk discounts that will help you add bulk discounts to products on your stores. It also has developed various other plugins like the popular plugin for managing the checkout form fields in WooCommerce, called Woocommerce Checkout Manager, which is highly feature-oriented yet lightweight and fast. There is also a free version of this plugin available in the WordPress directory named WooCommerce Checkout Field Editor.









 Login
Login
 Cart
Cart